Role of desumoylation in the development of prostate cancer
- PMID: 16925949
- PMCID: PMC1601940
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06445
Role of desumoylation in the development of prostate cancer
Abstract
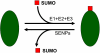
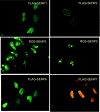
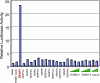
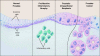
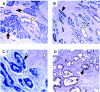
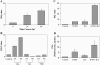
SUMO is a novel ubiquitin-like protein that can covalently modify a large number of nuclear proteins. SUMO modification has emerged as an important regulatory mechanism for protein function and localization. Sumoylation is a dynamic process that is mediated by activating (E1), conjugating (E2), and ligating (E3) enzymes and is readily reversed by a family of SUMO-specific proteases (SENPs). Since SUMO was discovered 10 years ago, the biologic contribution of this posttranslational modification has remained unclear. In this review, we report that SENP1, a member of the SENP family, is overexpressed in human prostate cancer specimens. The induction of SENP1 is observed with the chronic exposure of prostate cancer cells to androgen and/or interleukin (IL) 6. SENP1 upregulation modulates the transcriptional activity of androgen receptors (ARs) and c-Jun, as well as cyclin D1 expression. Initial in vivo data from transgenic mice indicate that overexpression of SENP1 in the prostate leads to the development of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia at an early age. Collectively, these studies indicate that overexpression of SENP1 is associated with prostate cancer development.
Figures








References
-
- Okura T, Gong L, Kamitani T, Wada T, Okura I, Wei CF, Chang HM, Yeh ET. Protection against Fas/APO-1- and tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death by a novel protein, sentrin. J Immunol. 1996;157:4277–4281. - PubMed
-
- Mahajan R, Delphin C, Guan T, Gerace L, Melchior F. A small ubiquitin-related polypeptide involved in targeting RanGAP1 to nuclear pore complex protein RanBP2. Cell. 1997;88:97–107. - PubMed
-
- Boddy MN, Howe K, Etkin LD, Solomon E, Freemont PS. PIC 1, a novel ubiquitin-like protein which interacts with the PML component of a multiprotein complex that is disrupted in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Oncogene. 1996;13:971–982. - PubMed
-
- Shen Z, Pardington-Purtymun PE, Comeaux JC, Moyzis RK, Chen DJ. UBL1, a human ubiquitin-like protein associating with human RAD51/RAD52 proteins. Genomics. 1996;36:271–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
