Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans outer membrane protein 100 triggers innate immunity and production of beta-defensin and the 18-kilodalton cationic antimicrobial protein through the fibronectin-integrin pathway in human gingival epithelial cells
- PMID: 16926414
- PMCID: PMC1594852
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00056-06
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans outer membrane protein 100 triggers innate immunity and production of beta-defensin and the 18-kilodalton cationic antimicrobial protein through the fibronectin-integrin pathway in human gingival epithelial cells
Abstract
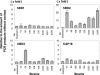
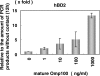
Antimicrobial peptides, human beta-defensin (hBD), and the 18-kDa cationic antimicrobial protein (CAP18) are components of innate immunity. These peptides have antimicrobial activity against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans is a gram-negative facultative anaerobe implicated in the initiation of periodontitis. The innate immunity peptides have antibacterial activity against A. actinomycetemcomitans. We investigated the molecular mechanism of human gingival epithelial cells (HGEC) responding to exposure to A. actinomycetemcomitans. HGEC constitutively express hBD1 and inducibly express hBD2, hBD3, and CAP18 on exposure to A. actinomycetemcomitans. The level of expression varies among clinical isolates. In the signaling pathway for hBD2 induction by the bacterial contact, we demonstrate that the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and not the NF-kappaB transcription factor pathway is used. We found the outer membrane protein 100 (Omp100; identified by molecular mass) is the component inducing the hBD2 response. Omp100 binds to fibronectin, an extracellular matrix inducing hBD2 via the MAP kinase pathway. Anti-integrin alpha(5)beta(1), antifibronectin, genistein, and PP2 suppress the Omp100-induced expression of hBD2, suggesting that Src kinase is involved through integrin alpha(5)beta(1). The inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6 and IL-8, produced by HGEC on contact with A. actinomycetemcomitans also stimulate expression of hBD2. Further, neutralizing antibody against TNF-alpha or IL-8 partially inhibits the induction of hBD2 on bacterial contact. Therefore, we found that the induction of the antimicrobial peptides is mediated by a direct response principally through an Omp100-fibronectin interaction, and using secondary stimulation by inflammatory cytokines induced by the bacterial exposure.
Figures







References
-
- Agerer, F., S. Lux, M. A., M. Rohde, K. Ohlsen, and C. R. Hauck. 2005. Cellular invasion by Staphylococcus aureus reveals a functional link between focal adhesion kinase and cortactin in integrin-mediated internalization. J. Cell Sci. 118:2189-2200. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa, R., H. Komatsuzawa, T. Kawai, S. Yamada, R. B. Goncalves, S. Izumi, T. Fujiwara, Y. Nakano, N. Suzuki, Y. Uchida, K. Ouhara, H. Shiba, M. A. Taubman, H. Kurihara, and M. Sugai. 2003. Outer membrane protein 100, a versatile virulence factor of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Mol. Microbiol. 50:1125-1139. - PubMed
-
- Asikainen, S., C. Chen, M. Saarela, L. Saxen, and J. Slots. 1997. Clonal specificity of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in destructive periodontal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 25(Suppl. 2):S227-S229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

