Pulmonary lymphatics are primary sites of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in guinea pigs infected by aerosol
- PMID: 16926435
- PMCID: PMC1594862
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00332-06
Pulmonary lymphatics are primary sites of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in guinea pigs infected by aerosol
Abstract
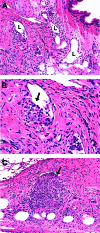
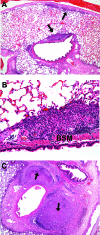
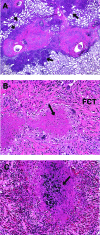
Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes a lymphatic vasculitis in the lungs of guinea pigs infected by a low-dose aerosol. This observation suggests that in addition to being a direct conduit from the lungs to the regional lymph nodes, pulmonary lymphatics are themselves sites of infection and could be the site of latent infection.
Figures


References
-
- Abadie, V., E. Badell, P. Douillard, D. Ensergueix, P. J. Leenen, M. Tanguy, L. Fiette, S. Saeland, B. Gicquel, and N. Winter. 2005. Neutrophils rapidly migrate via lymphatics after Mycobacterium bovis BCG intradermal vaccination and shuttle live bacilli to the draining lymph nodes. Blood 106:1843-1850. - PubMed
-
- Basaraba, R. J., D. D. Dailey, C. T. McFarland, C. A. Shanley, E. E. Smith, D. N. McMurray, and I. M. Orme. 2006. Lymphadenitis as a major element of disease in the guinea pig model of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinburgh) [Epub ahead of print.] - PubMed
-
- Dheda, K., H. Booth, J. F. Huggett, M. A. Johnson, A. Zumla, and G. A. Rook. 2005. Lung remodeling in pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Infect. Dis. 192:1201-1209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

