Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of once-daily saquinavir soft-gelatin capsule/ritonavir in antiretroviral-naive, HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 16926775
- PMCID: PMC1785231
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2652-8-2-36
Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of once-daily saquinavir soft-gelatin capsule/ritonavir in antiretroviral-naive, HIV-infected patients
Abstract
Context: Once-daily HIV treatment regimens are being used in clinical practice with the objective of improving patient acceptance and adherence.
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of saquinavir-soft-gelatin capsule (SGC)/ritonavir combination (1600 mg/100 mg) vs efavirenz (600 mg) both once daily and combined with 2 nucleoside analogs twice daily.
Setting: Twenty-six centers in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico.
Patients: A total of 171 antiretroviral naive HIV-infected individuals were enrolled in a 48-week, phase 3, open-label, randomized study.
Main outcome measure: Proportion of patients with HIV-RNA levels < 50 copies/mL. The pharmacokinetic profile of saquinavir-SGC was analyzed in a subset of randomly selected patients.
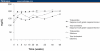
Results: In the primary intent-to-treat population at week 48, 51% (38/75) and 71% (55/77) of patients in the saquinavir-SGC/ritonavir and efavirenz groups, respectively, achieved HIV-RNA suppression < 50 copies/mL (P = .5392, 95% 1-sided confidence interval [CI] = -33.5%). In the on-treatment (OT) population, 73% (38/52) and 93% (54/58) of patients in the saquinavir-SGC/ritonavir and efavirenz groups, respectively, had effective viral suppression < 50 copies/mL (P = .5015, 95% 1-sided CI = -33.4%). Mean CD4+ cell counts increased by 239 and 204 cells/microliters (mcL), in the saquinavir-SGC/ritonavir and efavirenz groups, respectively, in the OT analysis (P = .058). Both regimens were reasonably well tolerated, although more gastrointestinal adverse events were reported with saquinavir-SGC/ritonavir. Pharmacokinetic profiles in 6 patients showed an observed median Cmin at 24 hours of 429 ng/mL (range, 68-1750 ng/mL).
Conclusions: Once-daily efavirenz was statistically superior to once-daily saquinavir-SGC/ritonavir. Gastrointestinal adverse effects were commonly associated with treatment failure in the saquinavir-SGC/ritonavir arm of the study.
Figures


References
-
- Palella FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Detels R, Munoz A, McFarlane G, et al. Effectiveness of potent antiretroviral therapy on time to AIDS and death in men with known HIV infection duration. AIDS Cohort Study Investigators. JAMA. 1998;280:1497–503. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JA, DeMasi R, Quinn J, et al. Overview of the effectiveness of triple combination therapy in antiretroviral-naive HIV-1 infected adults. AIDS. 2001;15:1369–1377. - PubMed
-
- Altice FL, Friedland GH. The era of adherence to HIV therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129:503–505. - PubMed
-
- Monforte d'Arminio A, Lepri AC, Rezza G, et al. Insights into the reasons for discontinuation of the first highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) regimen in a cohort of antiretroviral naive patients. I.CO.N.A. Study Group. Italian Cohort of Antiretroviral-Naive Patients. AIDS. 2000;14:499–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

