Immunomodulators as an antimicrobial tool
- PMID: 16931122
- PMCID: PMC7108246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.08.004
Immunomodulators as an antimicrobial tool
Abstract
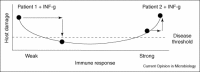
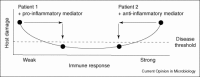
The spectrum of infectious diseases has shifted in the past 50 years to include those caused by microbes that cause disease predominantly in immunocompromised individuals. This phenomenon has underscored the dependence of microbial virulence on the immune status of the host. The limited efficacy of the available antimicrobial armamentarium in immunocompromised individuals, combined with increasing resistance to these agents, has led to an urgent need for new therapies for infectious diseases. Immunomodulation represents a novel approach to antimicrobial therapy that depends on bolstering host immunity, rather than direct antimicrobial activity. Immunomodulators can be divided into those that are specific to pathogens (pathogen-specific) and those that are not specific to pathogens (non-specific). However, to date only a few immunomodulators have been evaluated for their efficacy as antimicrobial tools.
Figures
References
-
- Committee on New Directions in the Study of Antimicrobial Therapeutics: Immunomodulation: Treating infectious diseases in a microbial world: report of two workshops on novel antimicrobial therapies. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2006. - PubMed
-
This 2006 National Academies report details the potential for modulating innate and acquired immunity and the microbiota to enhance the potential of immunomodulation for the treatment of infectious diseases.
-
- Datta K., Pirofski L. Towards a vaccine for Cryptococcus neoformans: principles and caveats. FEM Yeast Res. 2006;6:536. - PubMed
-
- Spellberg B., Powers J.H., Brass E.P., Miller L.G., Edwards J.E., Jr. Trends in antimicrobial drug development: implications for the future. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1279–1286. - PubMed
-
This article details decline in new drug development, despite the need for new additions to the available antimicrobial armamentarium, and puts forth a powerful argument in support of discovery of novel antimicrobial agents.
-
- Buchwald U.K., Pirofski L. Immune therapy for infectious diseases at the dawn of the 21(st) century: the past, present and future role of antibody therapy, therapeutic vaccination and biological response modifiers. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:945–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

