Systems analysis of effector caspase activation and its control by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- PMID: 16932741
- PMCID: PMC1570423
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601295
Systems analysis of effector caspase activation and its control by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
Abstract
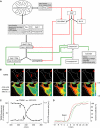
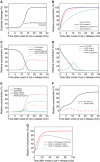
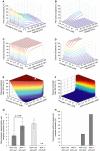
Activation of effector caspases is a final step during apoptosis. Single-cell imaging studies have demonstrated that this process may occur as a rapid, all-or-none response, triggering a complete substrate cleavage within 15 min. Based on biochemical data from HeLa cells, we have developed a computational model of apoptosome-dependent caspase activation that was sufficient to remodel the rapid kinetics of effector caspase activation observed in vivo. Sensitivity analyses predicted a critical role for caspase-3-dependent feedback signalling and the X-linked-inhibitor-of-apoptosis-protein (XIAP), but a less prominent role for the XIAP antagonist Smac. Single-cell experiments employing a caspase fluorescence resonance energy transfer substrate verified these model predictions qualitatively and quantitatively. XIAP was predicted to control this all-or-none response, with concentrations as high as 0.15 microM enabling, but concentrations >0.30 microM significantly blocking substrate cleavage. Overexpression of XIAP within these threshold concentrations produced cells showing slow effector caspase activation and submaximal substrate cleavage. Our study supports the hypothesis that high levels of XIAP control caspase activation and substrate cleavage, and may promote apoptosis resistance and sublethal caspase activation in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Arama E, Agapite J, Steller H (2003) Caspase activity and a specific cytochrome C are required for sperm differentiation in Drosophila. Dev Cell 4: 687–697 - PubMed
-
- Arnt CR, Chiorean MV, Heldebrant MP, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH (2002) Synthetic Smac/DIABLO peptides enhance the effects of chemotherapeutic agents by binding XIAP and cIAP1 in situ. J Biol Chem 277: 44236–44243 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

