Mammalian SWI/SNF complexes facilitate DNA double-strand break repair by promoting gamma-H2AX induction
- PMID: 16932743
- PMCID: PMC1560357
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601291
Mammalian SWI/SNF complexes facilitate DNA double-strand break repair by promoting gamma-H2AX induction
Abstract
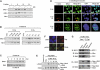
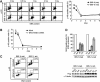
Although mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes have been well established to play important role in transcription, their role in DNA repair has remained largely unexplored. Here we show that inactivation of the SWI/SNF complexes and downregulation of the catalytic core subunits of the complexes both result in inefficient DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair and increased DNA damage sensitivity as well as a large defect in H2AX phosphorylation (gamma-H2AX) and nuclear focus formation after DNA damage. The expression of most DSB repair genes remains unaffected and DNA damage checkpoints are grossly intact in the cells inactivated for the SWI/SNF complexes. Although the SWI/SNF complexes do not affect the expression of ATM, DNA-PK and ATR, or their activation and/or recruitment to DSBs, they rapidly bind to DSB-surrounding chromatin via interaction with gamma-H2AX in the manner that is dependent on the amount of DNA damage. Given the crucial role for gamma-H2AX in efficient DSB repair, these results suggest that the SWI/SNF complexes facilitate DSB repair, at least in part, by promoting H2AX phosphorylation by directly acting on chromatin.
Figures
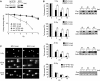

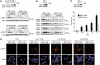
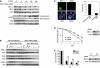
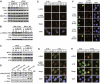
Similar articles
-
Human SNF5/INI1, a component of the human SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, promotes nucleotide excision repair by influencing ATM recruitment and downstream H2AX phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(23):6206-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00503-09. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19805520 Free PMC article.
-
ATM-mediated phosphorylation of the chromatin remodeling enzyme BRG1 modulates DNA double-strand break repair.Oncogene. 2015 Jan 15;34(3):303-13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.556. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24413084
-
Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes are required to prevent apoptosis after DNA damage.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Jan 1;8(1):29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.08.011. Epub 2008 Oct 7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 18822392
-
The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21036673 Review.
-
[gamma H2AX in the recognition of DNA double-strand breaks].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009 Feb 27;63:92-8. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009. PMID: 19252467 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of epigenetic modifiers in repair of DNA damage associated with chronic inflammatory diseases.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;780:69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.09.005. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31395351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cooperative activation loop among SWI/SNF, gamma-H2AX and H3 acetylation for DNA double-strand break repair.EMBO J. 2010 Apr 21;29(8):1434-45. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.27. Epub 2010 Mar 11. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20224553 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolin mediates nucleosome disruption critical for DNA double-strand break repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 15;110(42):16874-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306160110. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24082117 Free PMC article.
-
Vulnerabilities of mutant SWI/SNF complexes in cancer.Cancer Cell. 2014 Sep 8;26(3):309-317. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.018. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 25203320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SWI/SNF ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeler promotes resection initiation at a DNA double-strand break in yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):5887-5900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx221. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28398510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allard S, Masson JY, Cote J (2004) Chromatin remodeling and the maintenance of genome integrity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1677: 158–164 - PubMed
-
- Andegeko Y, Moyal L, Mittelman L, Tsarfaty I, Shiloh Y, Rotman G (2001) Nuclear retention of ATM at sites of DNA double strand breaks. J Biol Chem 276: 38224–38230 - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421: 499–506 - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2004) Initiating cellular stress responses. Cell 118: 9–17 - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Alt FW (2004) H2AX may function as an anchor to hold broken chromosomal DNA ends in close proximity. Cell Cycle 3: 149–153 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

