Modeling somatic evolution in tumorigenesis
- PMID: 16933983
- PMCID: PMC1550273
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020108
Modeling somatic evolution in tumorigenesis
Abstract
Tumorigenesis in humans is thought to be a multistep process where certain mutations confer a selective advantage, allowing lineages derived from the mutated cell to outcompete other cells. Although molecular cell biology has substantially advanced cancer research, our understanding of the evolutionary dynamics that govern tumorigenesis is limited. This paper analyzes the computational implications of cancer progression presented by Hanahan and Weinberg in The Hallmarks of Cancer. We model the complexities of tumor progression as a small set of underlying rules that govern the transformation of normal cells to tumor cells. The rules are implemented in a stochastic multistep model. The model predicts that (i) early-onset cancers proceed through a different sequence of mutation acquisition than late-onset cancers; (ii) tumor heterogeneity varies with acquisition of genetic instability, mutation pathway, and selective pressures during tumorigenesis; (iii) there exists an optimal initial telomere length which lowers cancer incidence and raises time of cancer onset; and (iv) the ability to initiate angiogenesis is an important stage-setting mutation, which is often exploited by other cells. The model offers insight into how the sequence of acquired mutations affects the timing and cellular makeup of the resulting tumor and how the cellular-level population dynamics drive neoplastic evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
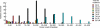


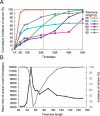
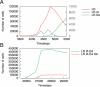

References
-
- Cahill DP, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Lengauer C. Genetic instability and Darwinian selection in tumours. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9:M57–M60. - PubMed
-
- Frank S, Nowak M. Problems of somatic mutation and cancer. BioEssays. 2004;26:291–299. - PubMed
-
- Nowell PC. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976;194:23–28. - PubMed
-
- Renan MJ. How many mutations are required for tumorigenesis? Implications from human cancer data. Mol Carcinog. 1993;7:139–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

