Ethanol sensitization in a neurodevelopmental lesion model of schizophrenia in rats
- PMID: 16934862
- PMCID: PMC2891031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2006.07.017
Ethanol sensitization in a neurodevelopmental lesion model of schizophrenia in rats
Abstract
Substance use disorder comorbidity in schizophrenia may reflect dysfunctional cortical-striatal-limbic circuitry commonly involved in the addiction process and the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Rats with neonatal ventral hippocampal lesions (NVHL) demonstrate post-adolescent onset of schizophrenia-like symptoms and increased addiction vulnerability in paradigms using cocaine in adulthood. Here, we investigated response profiles of young adult NVHL vs. SHAM rats to ethanol, an addictive drug with many psychopharmacological effects divergent from those of cocaine, in a locomotor sensitization paradigm. Over 15 days of daily injections of saline, low (0.15 g/kg) or high (1.0 g/kg) doses of ethanol, NVHL rats showed stimulatory effects at the low dose compared to saline and high-dose conditions, while SHAM rats showed expected patterns of dose-dependent suppression of locomotor activity. In a challenge session 2 weeks later in which a moderate dose (0.25 g/kg) of ethanol was given to all subjects, NVHL rats with history of prior ethanol exposure showed greater locomotor activity consistent with installment of alcohol-induced sensitization not present in SHAMs. These findings provide further evidence of enhanced short- and long-term responsivity to abused drugs in a neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia, and may reflect potentiation of common mechanisms of addiction shared between pharmacologically diverse addictive drugs.
Figures


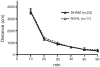
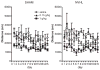

References
-
- Agabio R, Carai MAM, Lobina C, Pani M, Reali R, Vacca G, et al. Alcohol stimulates motor activity in selectively bred Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP), but not in Sardinian alcohol-nonpreferring (sNP), rats. Alcohol. 2001;23:123–6. - PubMed
-
- Becker A, Grecksch G. Haloperidol and clozapine affect social behavior in rats postnatally lesioned in the ventral hippocampus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003;76:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Becker A, Grecksch G, Bernstein H-G, Hollt V, Bogerts B. Social behavior in rats lesioned with ibotenic acid in the hippocampus: quantitative and qualitative analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1999;144:333–8. - PubMed
-
- Benes FM, Berretta S. GABAergic interneurons: implications for understanding schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001;25:1–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

