A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways
- PMID: 16935876
- PMCID: PMC1616954
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl550
A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways
Abstract
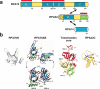
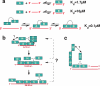
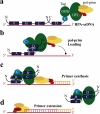
Processing of DNA in replication, repair and recombination pathways in cells of all organisms requires the participation of at least one major single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding protein. This protein protects ssDNA from nucleolytic damage, prevents hairpin formation and blocks DNA reannealing until the processing pathway is successfully completed. Many ssDNA-binding proteins interact physically and functionally with a variety of other DNA processing proteins. These interactions are thought to temporally order and guide the parade of proteins that 'trade places' on the ssDNA, a model known as 'hand-off', as the processing pathway progresses. How this hand-off mechanism works remains poorly understood. Recent studies of the conserved eukaryotic ssDNA-binding protein replication protein A (RPA) suggest a novel mechanism by which proteins may trade places on ssDNA by binding to RPA and mediating conformation changes that alter the ssDNA-binding properties of RPA. This article reviews the structure and function of RPA, summarizes recent studies of RPA in DNA replication and other DNA processing pathways, and proposes a general model for the role of RPA in protein-mediated hand-off.
Figures
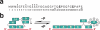
References
-
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. - PubMed
-
- Bullock P.A. The initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997;32:503–568. - PubMed
-
- Waga S., Stillman B. The DNA replication fork in eukaryotic cells. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:721–751. - PubMed
-
- Simmons D.T. SV40 large T antigen functions in DNA replication and transformation. Adv. Virus Res. 2000;55:75–134. - PubMed
-
- Stenlund A. Initiation of DNA replication: lessons from viral initiator proteins. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:777–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

