E- and P-selectins synergistically inhibit bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 16936251
- PMCID: PMC1698829
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060086
E- and P-selectins synergistically inhibit bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
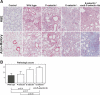
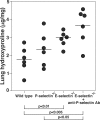
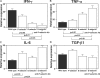
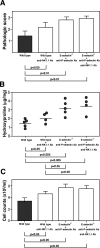
The development of bleomycin-induced lung injury, which is a model of pulmonary fibrosis, results from inflammatory cell infiltration, a process highly regulated by the expression of multiple adhesion molecules. Therefore, bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis was examined in E-selectin-/- mice, P-selectin-/- mice, and E-selectin-/- mice treated with anti-P-selectin monoclonal antibody (mAb) in comparison of wild-type mice. E-selectin-/- mice treated with anti-P-selectin mAb exhibited augmented lung fibrosis histologically, increased lung collagen deposition, and increased mortality compared to wild-type mice. Furthermore, lung interferon-gamma mRNA expression decreased in E-selectin-/- mice treated with anti-P-selectin mAb relative to wild-type mice, while tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 mRNA expression increased in these mice. Similar changes were observed in E-selectin-/- mice, albeit to a lesser extent than those treated with anti-P-selectin mAb. Remarkably, flow cytometric analysis revealed that the frequency of interferon-gamma-producing natural killer T (NKT) cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage was decreased in E-selectin-/- mice and E-selectin-/- mice treated with anti-P-selectin mAb compared with wild-type mice. Moreover, the majority of NKT cells expressed high levels of CXCR3, suggesting that NKT cell infiltration is also dependent on CXCR3 expression. These results suggest that E- and P-selectins synergistically inhibit lung fibrosis by promoting the recruitment of NKT cells.
Figures

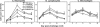
Similar articles
-
[Effects of andrographolide on the concentration of cytokines in BALF and the expressions of type I and III collagen mRNA in lung tissue in bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;27(7):725-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21722520 Chinese.
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and L-selectin regulate bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2002 Nov;161(5):1607-18. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64439-2. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12414509 Free PMC article.
-
[The pivotal role of CXCR3 in the pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2005 Jan;28(1):28-32. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15774188 Chinese.
-
Use of human amniotic epithelial cells in mouse models of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2018 May 17;13(5):e0197658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197658. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29772024 Free PMC article.
-
Bleomycin lung toxicity: who are the patients with increased risk?Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005;18(5):363-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.01.007. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15939315 Review.
Cited by
-
Muscle fatigue: MK2 signaling and myofibroblast differentiation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007 Nov;37(5):503-6. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0005ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17940320 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Inhalable Hsa-miR-30a-3p Liposomes Attenuate Pulmonary Fibrosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(19):e2405434. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405434. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40119620 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in SELE gene and risk of coal workers' pneumoconiosis in Chinese: a case-control study.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e73254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073254. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066042 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia vaccine-based immunotherapy arrests and reverses established pulmonary fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2016 Apr 7;1(4):e83116. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.83116. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27158671 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-asialo GM1 NK cell depleting antibody does not alter the development of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 12;9(6):e99350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099350. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24922516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paine R, III, Ward PA. Cell adhesion molecules and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Med. 1999;107:268–279. - PubMed
-
- Silver RM, Miller KS, Kinsella MB, Smith EA, Schabel SI. Evaluation and management of scleroderma lung disease using bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Med. 1990;88:470–476. - PubMed
-
- Tedder TF, Li X, Steeber DA. The selectins and their ligands: adhesion molecules of the vasculature. Adv Mol Cell Biol. 1999;28:65–111.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

