RecQ helicases: lessons from model organisms
- PMID: 16936315
- PMCID: PMC1616958
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl557
RecQ helicases: lessons from model organisms
Abstract
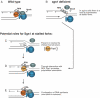
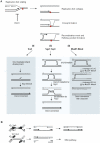
RecQ DNA helicases function during DNA replication and are essential for the maintenance of genome stability. There is increasing evidence that spontaneous genomic instability occurs primarily during DNA replication, and that proteins involved in the S-phase checkpoint are a principal defence against such instability. Cells that lack functional RecQ helicases exhibit phenotypes consistent with an inability to fully resume replication fork progress after encountering DNA damage or fork arrest. In this review we will concentrate on the various functions of RecQ helicases during S phase in model organisms.
Figures

References
-
- Hickson I.D. RecQ helicases: caretakers of the genome. Nature Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Ozgenc A., Loeb L.A. Current advances in unraveling the function of the Werner syndrome protein. Mutat. Res. 2005;577:237–251. - PubMed
-
- Morozov V., Mushegian A.R., Koonin E.V., Bork P. A putative nucleic acid-binding domain in Bloom's and Werner's syndrome helicases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997;22:417–418. - PubMed
-
- Heo S.J., Tatebayashi K., Ohsugi I., Shimamoto A., Furuichi Y., Ikeda H. Bloom's syndrome gene suppresses premature ageing caused by Sgs1 deficiency in yeast. Genes Cells. 1999;4:619–625. - PubMed

