Effects of Ca2+ channel blockers on store-operated Ca2+ channel currents of Kupffer cells after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 16937441
- PMCID: PMC4087835
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i29.4694
Effects of Ca2+ channel blockers on store-operated Ca2+ channel currents of Kupffer cells after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
Aim: To study the effects of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury on store-operated calcium channel (SOC) currents (I(SOC)) in freshly isolated rat Kupffer cells, and the effects of Ca(2+) channel blockers, 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB), SK and F96365, econazole and miconazole, on I(SOC) in isolated rat Kupffer cells after hepatic I/R injury.
Methods: The model of rat hepatic I/R injury was established. Whole-cell patch-clamp techniques were performed to investigate the effects of 2-APB, SK and F96365, econazole and miconazole on I(SOC) in isolated rat Kupffer cells after hepatic I /R injury.
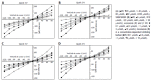
Results: I/R injury significantly increased I(SOC) from -80.4 +/- 25.2pA to -159.5 +/- 34.5pA ((b)P < 0.01, n = 30). 2-APB (20, 40, 60, 80, 100 micromol/L), SK and F96365 (5, 10, 20, 40, 50 micromol/L), econazole (0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 micromol/L) and miconazole (0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 micromol/L) inhibited I(SOC) in a concentration-dependent manner with IC50 of 37.41 micromol/L (n = 8), 5.89 micromol/L (n = 11), 0.21 micromol/L (n = 13), and 0.28 micromol/L (n = 10). The peak value of I(SOC) in the I-V relationship was decreased by the blockers in different concentrations, but the reverse potential of I(SOC) was not transformed.
Conclusion: SOC is the main channel for the influx of Ca(2+) during hepatic I/R injuries. Calcium channel blockers, 2-APB, SK and F96365, econazole and miconazole, have obviously protective effects on I/R injury, probably by inhibiting I(SOC) in Kupffer cells and preventing the activation of Kupffer cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of 2-APB on store-operated Ca2+ channel currents of hepatocytes after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2005;25(1):39-41. doi: 10.1007/BF02831382. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2005. PMID: 15934304
-
2-APB protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing cellular and mitochondrial calcium uptake.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):G623-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00521.2006. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17627971
-
Effects and mechanisms of store-operated calcium channel blockade on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jan 28;18(4):356-67. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i4.356. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22294842 Free PMC article.
-
2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release.FASEB J. 2002 Aug;16(10):1145-50. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0037rev. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12153982 Review.
-
Glycine: a new anti-inflammatory immunonutrient.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Nov 30;56(9-10):843-56. doi: 10.1007/s000180050030. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction Mechanisms Between Major Depressive Disorder and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 13;12:711835. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.711835. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34966296 Free PMC article.
-
Action of econazole on Ca2+ levels and cytotoxicity in OC2 human oral cancer cells.J Dent Sci. 2023 Jul;18(3):1280-1287. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.02.013. Epub 2023 Mar 6. J Dent Sci. 2023. PMID: 37404653 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Reduces Lipotoxicity-Induced Meta-Inflammation in β-Cells through the Activation of GPR40-PLC-IP3 Pathway.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Dec 18;2019:7602427. doi: 10.1155/2019/7602427. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31950065 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial pathway mediates the antileukemic effects of Hemidesmus indicus, a promising botanical drug.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021544. Epub 2011 Jun 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21738701 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial stress affects rat alveolar type II cell signaling and gene expression.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Jul;303(2):L117-29. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00340.2011. Epub 2012 May 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22610352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vazquez G, Wedel BJ, Aziz O, Trebak M, Putney JW Jr. The mammalian TRPC cation channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1742:21–36. - PubMed
-
- Penner R, Fleig A. Store-operated calcium entry: a tough nut to CRAC. Sci STKE. 2004;2004:pe38. - PubMed
-
- Putney JW Jr. Store-operated calcium channels: how do we measure them, and why do we care. Sci STKE. 2004;2004:pe37. - PubMed
-
- Gregory RB, Hughes R, Riley AM, Potter BV, Wilcox RA, Barritt GJ. Inositol trisphosphate analogues selective for types I and II inositol trisphosphate receptors exert differential effects on vasopressin-stimulated Ca2+ inflow and Ca2+ release from intracellular stores in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 2004;381:519–526. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

