Current and future applications of in vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy in hepatobiliary disease
- PMID: 16937457
- PMCID: PMC4087609
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4773
Current and future applications of in vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy in hepatobiliary disease
Abstract
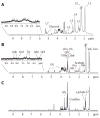
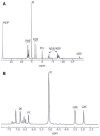
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy allows the study of cellular biochemistry and metabolism, both in the whole body in vivo and at higher magnetic field strengths in vitro. Since the technique is non-invasive and non-selective, magnetic resonance spectroscopy methodologies have been widely applied in biochemistry and medicine. In vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of cells, body fluids and tissues have been used in medical biochemistry to investigate pathophysiological processes and more recently, the technique has been used by physicians to determine disease abnormalities in vivo. This highlighted topic illustrates the potential of in vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy in studying the hepatobiliary system. The role of in vitro proton and phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the study of malignant and non-malignant liver disease and bile composition studies are discussed, particularly with reference to correlative in vivo whole-body magnetic resonance spectroscopy applications. In summary, magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques can provide non-invasive biochemical information on disease severity and pointers to underlying pathophysiological processes. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy holds potential promise as a screening tool for disease biomarkers, as well as assessing therapeutic response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vivo and in vitro nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy as a tool for investigating hepatobiliary disease: a review of H and P MRS applications.Liver Int. 2005 Apr;25(2):273-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2005.01090.x. Liver Int. 2005. PMID: 15780050 Review.
-
NMR spectroscopy for discovery and quantitation of biomarkers of disease in human bile.Bioanalysis. 2011 Aug;3(16):1877-90. doi: 10.4155/bio.11.152. Bioanalysis. 2011. PMID: 21877897 Review.
-
Applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy to chronic liver disease.Clin Med (Lond). 2001 Jan-Feb;1(1):54-60. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.1-1-54. Clin Med (Lond). 2001. PMID: 11358078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance based metabolomics and liver diseases: Recent advances and future clinical applications.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 7;22(1):417-26. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.417. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26755887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatobiliary pathology.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005 May;21(3):260-9. doi: 10.1097/01.mog.0000159820.78532.68. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15818145 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to study hepatic metabolism in diffuse liver diseases, diabetes and cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr 7;16(13):1577-86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i13.1577. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20355236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of choline concentration following liver cell apoptosis using 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar 14;18(10):1130-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i10.1130. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22416190 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling of bile in cholangiocarcinoma using in vitro magnetic resonance spectroscopy.HPB (Oxford). 2010 Aug;12(6):396-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00185.x. HPB (Oxford). 2010. PMID: 20662790 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological Developments for Metabolic NMR Spectroscopy from Cultured Cells to Tissue Extracts: Achievements, Progress and Pitfalls.Molecules. 2022 Jun 30;27(13):4214. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134214. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization of bile homeostasis using (1)H-NMR spectroscopy as a route for assessing liver cancer.Lipids. 2009 Jan;44(1):27-35. doi: 10.1007/s11745-008-3254-6. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Lipids. 2009. PMID: 18982376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloch F, Hansen WW, Packard ME. Nuclear induction. Physics Review. 1946;69:127.
-
- Jacobson B, Anderson WA, Arnold JT. A proton magnetic resonance study of the hydration of deoxyribonucleic acid. Nature. 1954;17:772–773.
-
- Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK. Metabonomics and its role in drug development and disease diagnosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2004;4:189–199. - PubMed
-
- Bollard ME, Stanley EG, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Holmes E. NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition. NMR Biomed. 2005;18:143–162. - PubMed
-
- Cox IJ, Menon DK, Sargentoni J, Bryant DJ, Collins AG, Coutts GA, Iles RA, Bell JD, Benjamin IS, Gilbey S. Phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the human liver using chemical shift imaging techniques. J Hepatol. 1992;14:265–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

