DA-9601, a standardized extract of Artemisia asiatica, blocks TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 and CCL20 production by inhibiting p38 kinase and NF-kappaB pathways in human gastric epithelial cells
- PMID: 16937467
- PMCID: PMC4087619
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4850
DA-9601, a standardized extract of Artemisia asiatica, blocks TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 and CCL20 production by inhibiting p38 kinase and NF-kappaB pathways in human gastric epithelial cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether, or how, DA-9601, which is a new gastroprotective agent, inhibits TNF-alpha-induced inflammatory signals in gastric epithelial AGS cells.
Methods: Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. IL-8 and CCL20 promoter activities were determined by a luciferase reporter gene assay. NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional activity was determined by I-kappaB alpha degradation, NF-kappaB p65 nuclear translocation and a luciferase activity assay. IL-8 and CCL20 gene expression and protein secretion were determined by RT-PCR and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Total and phosphorylated forms of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) were determined by Western blot.
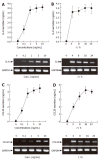
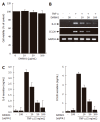
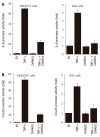
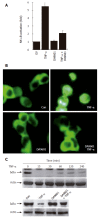
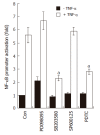
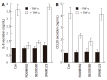
Results: Treatment of AGS cells with DA-9601 reduced TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 and CCL20 promoter activities, as well as their gene expression and protein release. TNF-alpha also induced NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional activity in AGS cells. In contrast, in cells treated with DA-9601, TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activity was significantly blocked. Although all three MAP kinase family members were phosphorylated in response to TNF-alpha, a selective inhibitor of p38 kinase SB203580 only could inhibit both NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional activity and IL-8 and CCL20 production, suggesting a potential link between p38 kinase and NF-kappaB-dependent pathways in AGS cells. Interestingly, DA-9601 also selectively inhibited p38 kinase phosphorylation induced by TNF-alpha.
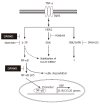
Conclusion: DA-9601 blocked TNF-alpha-mediated inflammatory signals by potentially modulating the p38 kinase pathway and/or a signal leading to NF-kappaB-dependent pathways in gastric epithelial cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extracellular nucleotides regulate CCL20 release from human primary airway epithelial cells, monocytes and monocyte-derived dendritic cells.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;211(3):716-27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20979. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17295217
-
Transcriptional regulation of lysophosphatidic acid-induced interleukin-8 expression and secretion by p38 MAPK and JNK in human bronchial epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2006 Feb 1;393(Pt 3):657-68. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050791. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16197369 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α regulates interleukin-33 expression through extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38, and nuclear factor-κB pathways in airway epithelial cells.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016 Sep;6(9):973-80. doi: 10.1002/alr.21761. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. PMID: 27060290
-
Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and gene regulation of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1185-95. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00412-3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007957 Review.
-
Rac mediates TNF-induced cytokine production via modulation of NF-kappaB.Mol Immunol. 2008 May;45(9):2446-54. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.12.011. Epub 2008 Feb 6. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18258304 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of eupatilin on Helicobacter pylori CagA-induced gastric inflammation.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 5;19(11):e0313251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313251. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39499687 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2-mediated mucoprotective and anti-inflammatory actions of Artemisia extracts led to attenuate stress related mucosal damages.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015 Mar;56(2):132-42. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.14-76. Epub 2014 Nov 28. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25759519 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds, Pharmacological Actions, and Pharmacokinetics of Wormwood (Artemisia absinthium).Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Jun 23;9(6):353. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9060353. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32585887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Plant-Derived Natural Products in the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-What Is the Clinical Evidence So Far?Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;13(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/life13081703. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical Effects of Artemisia Absinthium Ointment and Liniment in Comparison with Piroxicam Gel in Patients with Knee Joint Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial.Iran J Med Sci. 2017 Nov;42(6):524-531. Iran J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29184260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hahm KB, Kim JH, You BM, Kim YS, Cho SW, Yim H, Ahn BO, Kim WB. Induction of apoptosis with an extract of Artemisia asiatica attenuates the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. Pancreas. 1998;17:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Ryu BK, Ahn BO, Oh TY, Kim SH, Kim WB, Lee EB. Studies on protective effect of DA-9601, Artemisia asiatica extract, on acetaminophen- and CCl4-induced liver damage in rats. Arch Pharm Res. 1998;21:508–513. - PubMed
-
- Huh K, Kwon TH, Shin US, Kim WB, Ahn BO, Oh TY, Kim JA. Inhibitory effects of DA-9601 on ethanol-induced gastrohemorrhagic lesions and gastric xanthine oxidase activity in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;88:269–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

