BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 mutations in colorectal polyps and stool
- PMID: 16937524
- PMCID: PMC4088011
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5148
BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 mutations in colorectal polyps and stool
Abstract
Aim: To assess the feasibility of using BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 genes as stool-based molecular markers for detection of colorectal adenomas and hyperplastic polyps (HPs).
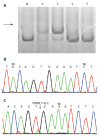
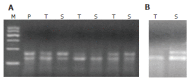
Methods: We applied PCR-SSCP and direct sequencing to detect BRAF mutations of polyps and paired stool samples. Primer-mediated restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis and mutant-enriched PCR were used in detection of K-ras mutations of polyp tissues and paired stool samples respectively. BAT26, a microsatellite instability marker was examined by detection of small unstable alleles in a poly (A) repeat.
Results: No genetic alterations were detected in the 36 colonoscopically normal patients in either tissues or stools. BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 mutations were found in 4 (16%), 10 (40%) and 3 (12%) of 25 adenoma tissues and among them, 75%, 80% and 100% of patients were observed to contain the same mutations in their corresponding stool samples. In HPs, mutations of BRAF and K-ras were detected in the tumor DNA of 2 (11.1%) and 8 (33.3%) of 18 patients respectively, all of whom had identical alterations in their stools. Taken together, the three genetic markers detected 15 (60%) of 25 adenomas and 8 (44.4%) of 18 HPs. The sensitivity of stool detection was 80% for adenomas and 100% for HPs with an overall specificity of 92% for adenomas and 100% for HPs.
Conclusion: BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 genes have the potential to be molecular markers for colorectal adenomas and HPs, and can be used as non-invasive screening markers for colorectal polyps.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyperplastic polyps and sessile serrated adenomas as a phenotypic expression of MYH-associated polyposis.Gastroenterology. 2008 Dec;135(6):2014-8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.020. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 19013464
-
Comparison of microsatellite instability, CpG island methylation phenotype, BRAF and KRAS status in serrated polyps and traditional adenomas indicates separate pathways to distinct colorectal carcinoma end points.Am J Surg Pathol. 2006 Dec;30(12):1491-501. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213313.36306.85. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17122504
-
Detection of K-ras mutations in stools of patients with colorectal cancer by mutant-enriched PCR.Int J Cancer. 1996 May 3;66(3):332-6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960503)66:3<332::AID-IJC11>3.0.CO;2-D. Int J Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8621253
-
Utilization of K-ras mutations identified in stool DNA for the early detection of colorectal cancer.J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2000;34:35-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4644(2000)77:34+<35::aid-jcb8>3.0.co;2-w. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2000. PMID: 10762013 Review.
-
Molecular approaches for colorectal cancer screening.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Mar;10(3):213-7. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199803000-00004. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998. PMID: 9585023 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular markers of carcinogenesis for risk stratification of individuals with colorectal polyps: a case-control study.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014 Oct;7(10):1023-34. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0140. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014. PMID: 25092825 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of stool DNA testing for multiple markers of colorectal cancer and advanced adenoma: a meta-analysis.Can J Gastroenterol. 2013 Aug;27(8):467-75. doi: 10.1155/2013/258030. Can J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23936877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical impact of serrated colorectal polyps.Clin Epidemiol. 2017 Feb 22;9:113-125. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S106257. eCollection 2017. Clin Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28260946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith RA, Cokkinides V, Eyre HJ. American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:11–25; quiz 49-50. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159–170. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins NJ, Bariol C, Ward RL. The serrated neoplasia pathway. Pathology. 2002;34:548–555. - PubMed
-
- Jass JR, Whitehall VL, Young J, Leggett BA. Emerging concepts in colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:862–876. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins NJ, Ward RL. Sporadic colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability and their possible origin in hyperplastic polyps and serrated adenomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1307–1313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

