BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 mutations in colorectal polyps and stool
- PMID: 16937524
- PMCID: PMC4088011
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5148
BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 mutations in colorectal polyps and stool
Abstract
Aim: To assess the feasibility of using BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 genes as stool-based molecular markers for detection of colorectal adenomas and hyperplastic polyps (HPs).
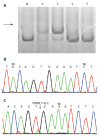
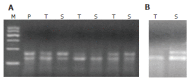
Methods: We applied PCR-SSCP and direct sequencing to detect BRAF mutations of polyps and paired stool samples. Primer-mediated restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis and mutant-enriched PCR were used in detection of K-ras mutations of polyp tissues and paired stool samples respectively. BAT26, a microsatellite instability marker was examined by detection of small unstable alleles in a poly (A) repeat.
Results: No genetic alterations were detected in the 36 colonoscopically normal patients in either tissues or stools. BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 mutations were found in 4 (16%), 10 (40%) and 3 (12%) of 25 adenoma tissues and among them, 75%, 80% and 100% of patients were observed to contain the same mutations in their corresponding stool samples. In HPs, mutations of BRAF and K-ras were detected in the tumor DNA of 2 (11.1%) and 8 (33.3%) of 18 patients respectively, all of whom had identical alterations in their stools. Taken together, the three genetic markers detected 15 (60%) of 25 adenomas and 8 (44.4%) of 18 HPs. The sensitivity of stool detection was 80% for adenomas and 100% for HPs with an overall specificity of 92% for adenomas and 100% for HPs.
Conclusion: BRAF, K-ras and BAT26 genes have the potential to be molecular markers for colorectal adenomas and HPs, and can be used as non-invasive screening markers for colorectal polyps.
Figures
References
-
- Smith RA, Cokkinides V, Eyre HJ. American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:11–25; quiz 49-50. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159–170. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins NJ, Bariol C, Ward RL. The serrated neoplasia pathway. Pathology. 2002;34:548–555. - PubMed
-
- Jass JR, Whitehall VL, Young J, Leggett BA. Emerging concepts in colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:862–876. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins NJ, Ward RL. Sporadic colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability and their possible origin in hyperplastic polyps and serrated adenomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1307–1313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

