Phospholipid scramblase-3 regulates cardiolipin de novo biosynthesis and its resynthesis in growing HeLa cells
- PMID: 16939411
- PMCID: PMC1698660
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060373
Phospholipid scramblase-3 regulates cardiolipin de novo biosynthesis and its resynthesis in growing HeLa cells
Abstract
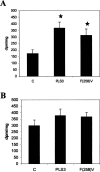
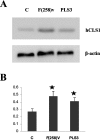
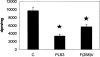
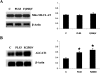
PLS3 (phospholipid scramblase-3) is a new member of the family of phospholipid scramblases and transports CL (cardiolipin) from the inner to the outer mitochondrial membrane. In the present paper we examined whether changing the levels of functional PLS3 in HeLa cells altered de novo CL biosynthesis and its resynthesis. HeLa cells overexpressing PLS3 or expressing a disrupted PLS3 (F258V) or control were incubated with [1,3-3H]glycerol and radioactivity incorporated into CL was determined. CL biosynthesis from [1,3-3H]glycerol was increased 1.8-fold in PLS3 cells and 2.1-fold in F258V cells compared with control. This was due to a 64% (P<0.05) and 2.6-fold (P<0.05) elevation in CL synthase activity in PLS3 and F258V cells respectively, compared with control, and not due to changes in phosphatidylglycerolphosphate synthase activity. The increase in CL synthase activity in these cells was due to an increase in its mRNA expression. In contrast, resynthesis of CL from [1-14C]linoleic acid was reduced 52% (P<0.05) in PLS3 and 45% (P<0.05) in F258V cells compared with control and this was due to a reduction in mitochondrial monolysocardiolipin acyltransferase activity. Although protein levels of mitochondrial monolysocardiolipin acyltransferase were unaltered, activity and mRNA expression of endoplasmic reticulum monolysocardiolipin acyltransferase was upregulated in PLS3 and F258V cells compared with controls. These data indicate that the CL resynthesis in HeLa cells is sensitive to the mitochondrial localization of CL and not the level of the reacylating enzymes. Alterations in functional PLS3 levels in PLS3 or F258V cells did not affect the mitochondrial decarboxylation of phosphatidylserine to phosphatidylethanolamine indicating that the biosynthetic changes to CL were specific for this mitochondrial phospholipid. We hypothesize that the cardiolipin resynthesis machinery in the cell 'senses' altered levels of CL on mitochondrial membranes and that de novo CL biosynthesis is up-regulated in HeLa cells as a compensatory mechanism in response to altered movement of mitochondrial CL. The results identify PLS3 as a novel regulator of CL de novo biosynthesis and its resynthesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
On the mechanism of the increase in cardiolipin biosynthesis and resynthesis in hepatocytes during rat liver regeneration.Biochem J. 2005 Feb 15;386(Pt 1):137-43. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040655. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15458384 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid scramblase 3 controls mitochondrial structure, function, and apoptotic response.Mol Cancer Res. 2003 Oct;1(12):892-902. Mol Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14573790
-
Mitochondrial monolysocardiolipin acyltransferase is elevated in the surviving population of H9c2 cardiac myoblast cells exposed to 2-deoxyglucose-induced apoptosis.Biochem Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;86(1):11-20. doi: 10.1139/o07-156. Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18364741
-
Cell biology of cardiac mitochondrial phospholipids.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;82(1):99-112. doi: 10.1139/o03-074. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15052331 Review.
-
Trypanosoma brucei: a model micro-organism to study eukaryotic phospholipid biosynthesis.FEBS J. 2011 Apr;278(7):1035-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08012.x. Epub 2011 Feb 3. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21232016 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiolipin synthase-1 mRNA expression does not correlate with endogenous cardiolipin synthase enzyme activity in vitro and in vivo in mammalian lipopolysaccharide models of inflammation.Inflammation. 2011 Aug;34(4):247-54. doi: 10.1007/s10753-010-9230-3. Inflammation. 2011. PMID: 20652826
-
Role of Cardiolipin in Mitochondrial Signaling Pathways.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Sep 29;5:90. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00090. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 29034233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberine Inhibits Oxygen Consumption Rate Independent of Alteration in Cardiolipin Levels in H9c2 Cells.Lipids. 2017 Nov;52(11):961-967. doi: 10.1007/s11745-017-4300-z. Epub 2017 Sep 23. Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28942573
-
Cardiolipin and its different properties in mitophagy and apoptosis.J Histochem Cytochem. 2015 May;63(5):301-11. doi: 10.1369/0022155415574818. Epub 2015 Feb 11. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015. PMID: 25673287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A striking parallel between cardiolipin fatty acid composition and phylogenetic belonging in marine bivalves: a possible adaptative evolution?Lipids. 2008 Oct;43(10):961-70. doi: 10.1007/s11745-008-3219-9. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Lipids. 2008. PMID: 18716818
References
-
- White D. A. The phospholipid composition of mammalian tissues. In: Ansell G. B., Hawthorne J. N., Dawson R. M. C., editors. Form and Function of Phospholipids. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1973. pp. 441–482.
-
- Hostetler K. Y. Polyglycerolphospholipids. In: Hawthorne J. N., Ansell G. B., editors. Phospholipids. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1982. pp. 215–242.
-
- Hoch F. L. Cardiolipins and biomembrane function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1992;1113:71–133. - PubMed
-
- Hatch G. M. Cell biology of cardiac mitochondrial phospholipids. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;82:99–112. - PubMed
-
- Schlame M., Rua D., Greenberg M. L. The biosynthesis and functional role of cardiolipin. Prog. Lipid Res. 2000;39:257–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

