Intracellular penetration and activity of DX-619 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- PMID: 16940122
- PMCID: PMC1563540
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00427-06
Intracellular penetration and activity of DX-619 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Abstract
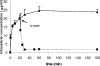
The intracellular penetration and activity of DX-619 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes have been evaluated. DX-619 reached intracellular concentrations 10 times higher than the extracellular concentrations reached. Uptake was rapid, reversible, nonsaturable, and affected by environmental temperature, some metabolic inhibitors, and a soluble membrane activator. DX-619 showed intracellular activity against Staphylococcus aureus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intracellular penetration and activity of BAY Y 3118 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Oct;38(10):2426-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.38.10.2426. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994. PMID: 7840582 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake and intracellular activity of sparfloxacin in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and tissue culture cells.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1053-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.36.5.1053. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992. PMID: 1324636 Free PMC article.
-
Potency of DX-619, a novel des-F(6)-quinolone, in haematogenous murine bronchopneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006 Sep;28(3):212-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2006.03.026. Epub 2006 Aug 2. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006. PMID: 16887340
-
[Intracellular penetration of 5 quinolones into non-phagocytic cells].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1996 Mar;14(3):167-70. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1996. PMID: 8695686 Spanish.
-
[Penetration of antibiotics into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes].Rev Esp Quimioter. 2002 Jun;15(2):129-40. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2002. PMID: 12582441 Review. Spanish. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baltch, A. L., L. H. Bopp, R. P. Smith, P. B. Michelsen, and W. J. Ritz. 2005. Antibacterial activities of gemifloxacin, levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin and erythromycin against intracellular Legionella pneumophila and Legionella micdadei in human monocytes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56:104-109. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda, Y., K. Yanagihara, H. Ohno, Y. Higashiyama, Y. Miyazaki, K. Tsukamoto, Y. Hirakata, K. Tomono, Y. Mizuta, T. Tashiro, and S. Kohno. 2006. In vivo efficacies and pharmacokinetics of DX-619, a novel des-fluoro(6) quinolone, against Streptococcus pneumoniae in a mouse lung infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:121-125. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

