Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen interacts with bromodomain protein Brd4 on host mitotic chromosomes
- PMID: 16940503
- PMCID: PMC1563901
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00502-06
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen interacts with bromodomain protein Brd4 on host mitotic chromosomes
Abstract
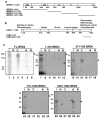
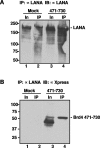
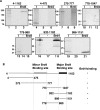
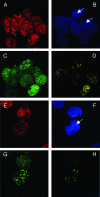
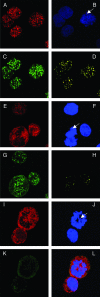
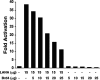
The latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is required for viral episome maintenance in host cells during latent infection. Two regions of the protein have been implicated in tethering LANA/viral episomes to the host mitotic chromosomes, and LANA chromosome-binding sites are subjects of high interest. Because previous studies had identified bromodomain protein Brd4 as the mitotic chromosome anchor for the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein, which tethers the viral episomes to host mitotic chromosomes (J. You, J. L. Croyle, A. Nishimura, K. Ozato, and P. M. Howley, Cell 117:349-360, 2004, and J. You, M. R. Schweiger, and P. M. Howley, J. Virol. 79:14956-14961, 2005), we examined whether KSHV LANA interacts with Brd4. We found that LANA binds Brd4 in vivo and in vitro and that the binding is mediated by a direct protein-protein interaction between the ET (extraterminal) domain of Brd4 and a carboxyl-terminal region of LANA previously implicated in chromosome binding. Brd4 associates with mitotic chromosomes throughout mitosis and demonstrates a strong colocalization with LANA and the KSHV episomes on host mitotic chromosomes. Although another bromodomain protein, RING3/Brd2, binds to LANA in a similar fashion in vitro, it is largely excluded from the mitotic chromosomes in KSHV-uninfected cells and is partially recruited to the chromosomes in KSHV-infected cells. These data identify Brd4 as an interacting protein for the carboxyl terminus of LANA on mitotic chromosomes and suggest distinct functional roles for the two bromodomain proteins RING3/Brd2 and Brd4 in LANA binding. Additionally, because Brd4 has recently been shown to have a role in transcription, we examined whether Brd4 can regulate the CDK2 promoter, which can be transactivated by LANA.
Figures
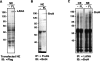

References
-
- Ballestas, M. E., P. A. Chatis, and K. M. Kaye. 1999. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 284:641-644. - PubMed
-
- Barbera, A. J., J. V. Chodaparambil, B. Kelley-Clarke, V. Joukov, J. C. Walter, K. Luger, and K. M. Kaye. 2006. The nucleosomal surface as a docking station for Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA. Science 311:856-861. - PubMed
-
- Bastien, N., and A. A. McBride. 2000. Interaction of the papillomavirus E2 protein with mitotic chromosomes. Virology 270:124-134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

