Intrapleural hypotonic cisplatin treatment for malignant pleural effusion in 80 patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a multi-institutional phase II trial
- PMID: 16940982
- PMCID: PMC2360516
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603319
Intrapleural hypotonic cisplatin treatment for malignant pleural effusion in 80 patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a multi-institutional phase II trial
Abstract
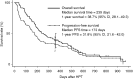
To assess the effect and toxicity of hypotonic cisplatin treatment (HPT) consisting of the intrapleural administration of cisplatin in distilled water for malignant pleural effusion in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Non-small-cell lung cancer patients with cytologically proven and previously untreated malignant pleural effusion were enrolled into this study. Firstly, the lung was fully re-expanded by a tube thoracostomy, and then 25 mg cisplatin in 500 ml of distilled water was instilled through a chest tube and then the tube was clamped. After 1 h, the tube was declamped and allowed to drain. The chest tube was removed when the pleural effusion volume decreased to 200 ml or less per day. A complete response (CR) was considered to occur when the pleural effusion disappeared. A partial response (PR) was determined to occur when the volume of pleural effusion remained under (1/4) of hemithorax. The response at 4 weeks was evaluated by an extramural review. Out of 84 patients enrolled from February 1998 to August 2002, 80 patients were eligible and analysed in the present study. The toxicity of HPT was acceptable. Neither a haematological toxicity of any grade nor grade 4 nonhaematological toxicity was observed. Grade 3 nonhaematological toxicities were observed, including nausea (4%), vomiting (3%), pyothorax (1%) and dyspnoea (1%). The median time of drainage from HTP was 4 days. Twenty-seven (34%) and 39 (49%) patients achieved CR and PR, respectively, for an overall response rate of 83% (95% confidence interval, 74-91%). The median duration of the response was 206 days. The median survival time of all patients was 239 days. Hypotonic cisplatin treatment for malignant pleural effusion of NSCLC is therefore considered to be feasible and effective. A phase III study of HPT is thus warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrapleural administration of cisplatin and etoposide to treat malignant pleural effusions in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Chemotherapy. 1999 May-Jun;45(3):197-204. doi: 10.1159/000007183. Chemotherapy. 1999. PMID: 10224342
-
Intrapleural cisplatin and cytarabine in the management of malignant pleural effusions: a Lung Cancer Study Group trial.J Clin Oncol. 1991 Feb;9(2):313-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.2.313. J Clin Oncol. 1991. PMID: 1988578 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypotonic cisplatin treatment for carcinomatous pleuritis found at thoracotomy in patients with lung cancer. In vitro experiments and preliminary clinical results.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993 Jun;105(6):1041-6. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993. PMID: 8388966 Clinical Trial.
-
Intrapleural chemotherapy without pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusions. LCSG Trial 861.Chest. 1994 Dec;106(6 Suppl):363S-366S. Chest. 1994. PMID: 7988265 Review.
-
Management of malignant pleural effusion by suicide gene therapy in advanced stage lung cancer: a case series and literature review.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Sep;19(9):593-600. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.36. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22744209 Review.
Cited by
-
[Therapeutical effects of pleural injecting recombinant human endostain to malignant pleural effusion nude mice model].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 May;18(5):266-71. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.05.03. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25975296 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Successful treatment of lung adenocarcinoma in an 18-year-old man.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011 Sep;59(9):616-8. doi: 10.1007/s11748-010-0730-8. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 22231790
-
Hollow boron nitride nanospheres as boron reservoir for prostate cancer treatment.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 6;8:13936. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13936. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28059072 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of osmolality for cancer treatment.J Physiol Sci. 2017 May;67(3):353-360. doi: 10.1007/s12576-017-0528-x. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Physiol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28185236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrapleural chemotherapy improves the survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients with positive pleural lavage cytology.Surg Today. 2013 Jun;43(6):648-53. doi: 10.1007/s00595-012-0281-y. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Surg Today. 2013. PMID: 22855011
References
-
- Chernow B, Sahn SA (1977) Carcinomatous involvement of the pleura: an analysis of 96 patients. Am J Med 63: 695–702 - PubMed
-
- Desai SD, Figueredo A (1979) Intracavitary doxorubicin in malignant effusions. Lancet 1: 872 (letter) - PubMed
-
- Hartman DL, Gaither JM, Kesler KA, Mylet DM, Brown JW, Mathur PN (1993) Comparison of insufflated talc under thoracoscopic guidance with standard tetracycline and bleomycin pleurodesis for control of malignant pleural effusions. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 105: 743–747 (discussion 747–748) - PubMed
-
- Hausheer FH, Yarbro JW (1985) Diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural effusion. Semin Oncol 12: 54–75 - PubMed
-
- Holoye PY, Jeffries DG, Dhingra HM, Holmes FA, Raber M, Engineer MS, Newman RA (1990) Intrapleural etoposide for malignant effusion. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 26: 147–150 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials