Hydrogen peroxide upregulates TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression in human astroglial cells, and augments apoptosis of T cells
- PMID: 16941746
- PMCID: PMC2687737
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.4.551
Hydrogen peroxide upregulates TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression in human astroglial cells, and augments apoptosis of T cells
Abstract
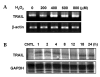
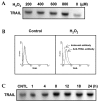
The brain is particularly vulnerable to oxygen free radicals, and these radicals have been implicated in the pathology of several neurological disorders. In this study, the modulation of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression by oxidative stress was shown in LN215 cells, an astroglioma cell line. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) treatment increased TRAIL expression in LN215 cells and H2O2-induced TRAIL augmented apoptosis in Peer cells, a cell line sensitive to TRAIL- mediated cell death. Our findings suggest that the upregulation of TRAIL in astroglial cells may abrogate immune cell effector functions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hydrogen peroxide enhances TRAIL-induced cell death through up-regulation of DR5 in human astrocytic cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Aug 8;372(4):870-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.148. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18534188
-
Lipopolysaccharides-activated human astroglioma cells induce apoptotic death of T-lymphocytes via c-Jun N-terminal kinases-dependent up-regulation of TRAIL.Neurosci Res. 2006 Apr;54(4):338-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2005.12.011. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16442178
-
The farnesyltransferase inhibitor R115777 up-regulates the expression of death receptor 5 and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2007 May 15;67(10):4973-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4044. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17510428
-
Murine TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand) expression induced by T cell activation is blocked by rapamycin, cyclosporin A, and inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, protein kinase C, and protein tyrosine kinases: evidence for TRAIL induction via the T cell receptor signaling pathway.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Oct 10;252(1):96-103. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4631. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10502402
-
Tunicamycin sensitizes human melanoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of TRAIL-R2 via the unfolded protein response.Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 15;67(12):5880-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0213. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17575157
Cited by
-
Cytotoxicity of probiotics from Philippine commercial dairy products on cancer cells and the effect on expression of cfos and cjun early apoptotic-promoting genes and Interleukin-1 β and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α proinflammatory cytokine genes.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:491740. doi: 10.1155/2014/491740. Epub 2014 Sep 7. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25276792 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNA-mRNA regulatory network associated with oxidative DNA damage in human astrocytes.ASN Neuro. 2022 Jan-Dec;14:17590914221101704. doi: 10.1177/17590914221101704. ASN Neuro. 2022. PMID: 35570825 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041102. Epub 2012 Jul 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22829912 Free PMC article.
-
Does each Component of Reactive Oxygen Species have a Dual Role in the Tumor Microenvironment?Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(31):4958-4986. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230719142202. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37469162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R, Dixit VM. An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science. 1997;277:815–818. - PubMed
-
- Wajant H, Johannes FJ, Haas E, Siemienski K, Schwenzer R, Schubert G, et al. Dominant-negative FADD inhibits TNFR60-, Fas/Apo1- and TRAIL-R/Apo2-mediated cell death but not gene induction. Curr Biol. 1998;8:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J, et al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science. 1997;276:111–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

