Probe set algorithms: is there a rational best bet?
- PMID: 16942624
- PMCID: PMC1569879
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-395
Probe set algorithms: is there a rational best bet?
Abstract
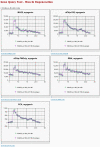
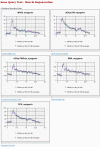
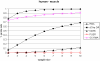
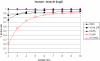
Affymetrix microarrays have become a standard experimental platform for studies of mRNA expression profiling. Their success is due, in part, to the multiple oligonucleotide features (probes) against each transcript (probe set). This multiple testing allows for more robust background assessments and gene expression measures, and has permitted the development of many computational methods to translate image data into a single normalized "signal" for mRNA transcript abundance. There are now many probe set algorithms that have been developed, with a gradual movement away from chip-by-chip methods (MAS5), to project-based model-fitting methods (dCHIP, RMA, others). Data interpretation is often profoundly changed by choice of algorithm, with disoriented biologists questioning what the "accurate" interpretation of their experiment is. Here, we summarize the debate concerning probe set algorithms. We provide examples of how changes in mismatch weight, normalizations, and construction of expression ratios each dramatically change data interpretation. All interpretations can be considered as computationally appropriate, but with varying biological credibility. We also illustrate the performance of two new hybrid algorithms (PLIER, GC-RMA) relative to more traditional algorithms (dCHIP, MAS5, Probe Profiler PCA, RMA) using an interactive power analysis tool. PLIER appears superior to other algorithms in avoiding false positives with poorly performing probe sets. Based on our interpretation of the literature, and examples presented here, we suggest that the variability in performance of probe set algorithms is more dependent upon assumptions regarding "background", than on calculations of "signal". We argue that "background" is an enormously complex variable that can only be vaguely quantified, and thus the "best" probe set algorithm will vary from project to project.
Figures
References
-
- Affymetrix http://www.affymetrix.com/
-
- Probe Profiler Software http://www.corimbia.com/Pages/ProbeProfiler.htm
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

