The selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A reduces nicotine-enhanced brain reward and nicotine-paired environmental cue functions
- PMID: 16942635
- PMCID: PMC3732043
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145706006560
The selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A reduces nicotine-enhanced brain reward and nicotine-paired environmental cue functions
Abstract
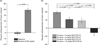
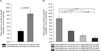
Increasing evidence suggests that enhanced dopamine (DA) neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) may play a role in mediating the reward and reinforcement produced by addictive drugs and in the attentional processing of drug-associated environmental cues. The meso-accumbens DA system is selectively enriched with DA D3 receptors, a DA receptor subtype increasingly implicated in reward-related brain and behavioural processes. From a variety of evidence, it has been suggested that selective DA D3 receptor antagonism may be a useful pharmacotherapeutic approach for treating addiction. The present experiments tested the efficacy of SB-277011A, a selective DA D3 receptor antagonist, in rat models of nicotine-enhanced electrical brain-stimulation reward (BSR), nicotine-induced conditioned locomotor activity (LMA), and nicotine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP). Nicotine was given subcutaneously within the dose range of 0.25-0.6 mg/kg (nicotine-free base). SB-277011A, given intraperitoneally within the dose range of 1-12 mg/kg, dose-dependently reduced nicotine-enhanced BSR, nicotine-induced conditioned LMA, and nicotine-induced CPP. The results suggest that selective D3 receptor antagonism constitutes a new and promising pharmacotherapeutic approach to the treatment of nicotine dependence.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of the selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A on the reinforcing effects of nicotine as measured by a progressive-ratio schedule in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Mar 22;559(2-3):173-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.004. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17303116
-
The selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists SB-277011A and NGB 2904 and the putative partial D3 receptor agonist BP-897 attenuate methamphetamine-enhanced brain stimulation reward in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Mar;196(4):533-42. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-0986-6. Epub 2007 Nov 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 17985117 Free PMC article.
-
YQA14: a novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist that inhibits cocaine self-administration in rats and mice, but not in D3 receptor-knockout mice.Addict Biol. 2012 Mar;17(2):259-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00317.x. Epub 2011 Apr 20. Addict Biol. 2012. PMID: 21507153 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological actions of NGB 2904, a selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, in animal models of drug addiction.CNS Drug Rev. 2007 Summer;13(2):240-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2007.00013.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 17627675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current perspectives on selective dopamine D(3) receptor antagonists as pharmacotherapeutics for addictions and related disorders.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Feb;1187:4-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05149.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20201845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine DRD2 and DRD3 Polymorphisms Involvement in Nicotine Dependence in Patients with Treatment-Resistant Mental Disorders.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 2;12(4):565. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040565. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35455685 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D3 Receptor Antagonism Reverses the Escalation of Oxycodone Self-administration and Decreases Withdrawal-Induced Hyperalgesia and Irritability-Like Behavior in Oxycodone-Dependent Heterogeneous Stock Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Jan 14;13:292. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00292. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31992976 Free PMC article.
-
Addiction and brain reward and antireward pathways.Adv Psychosom Med. 2011;30:22-60. doi: 10.1159/000324065. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Adv Psychosom Med. 2011. PMID: 21508625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise Pills for Drug Addiction: Forced Moderate Endurance Exercise Inhibits Methamphetamine-Induced Hyperactivity through the Striatal Glutamatergic Signaling Pathway in Male Sprague Dawley Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 30;22(15):8203. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158203. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360969 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D(3) receptor antagonist SB-277011A inhibits methamphetamine self-administration and methamphetamine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Jun 1;659(2-3):187-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.02.046. Epub 2011 Apr 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21466803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreoli M, Marcon C, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA. Effect of selective antagonism of dopamine D3 receptor by SB-277011-A on oral alcohol self-administration in mice. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003a;13(Suppl. 1):S17.
-
- Andreoli M, Tessari M, Pilla M, Valerio E, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA. Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors prevents nicotine-triggered relapse to nicotine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003b;28:1272–1280. - PubMed
-
- Ashby CR, Jr, Paul M, Gardner EL, Gerasimov MR, Dewey SL, Lennon IC, Taylor SJC. Systemic administration of 1R,4S-4-amino-cyclopent-2-ene-carboxylic acid, a reversible inhibitor of GABA transaminase, blocks expression of conditioned place preference to cocaine and nicotine in rats. Synapse. 2002;44:61–63. - PubMed
-
- Ashby CR, Jr, Paul M, Gardner EL, Heidbreder CA, Hagan JJ. Acute administration of the selective D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A blocks the acquisition and expression of the conditioned place preference response to heroin in male rats. Synapse. 2003;48:154–156. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Specio SE, Khroyan TV, Neisewander JL. Effects of intraaccumbens administration of SCH-23390 on cocaine-induced locomotion and conditioned place preference. Synapse. 1998;30:181–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

