A survey of essential gene function in the yeast cell division cycle
- PMID: 16943325
- PMCID: PMC1635385
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-04-0368
A survey of essential gene function in the yeast cell division cycle
Abstract
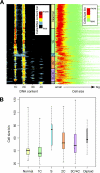
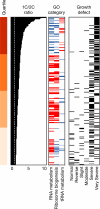
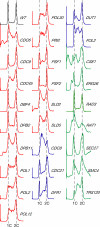
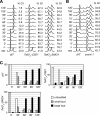
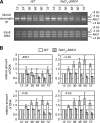
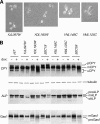
Mutations impacting specific stages of cell growth and division have provided a foundation for dissecting mechanisms that underlie cell cycle progression. We have undertaken an objective examination of the yeast cell cycle through flow cytometric analysis of DNA content in TetO(7) promoter mutant strains representing 75% of all essential yeast genes. More than 65% of the strains displayed specific alterations in DNA content, suggesting that reduced function of an essential gene in most cases impairs progression through a specific stage of the cell cycle. Because of the large number of essential genes required for protein biosynthesis, G1 accumulation was the most common phenotype observed in our analysis. In contrast, relatively few mutants displayed S-phase delay, and most of these were defective in genes required for DNA replication or nucleotide metabolism. G2 accumulation appeared to arise from a variety of defects. In addition to providing a global view of the diversity of essential cellular processes that influence cell cycle progression, these data also provided predictions regarding the functions of individual genes: we identified four new genes involved in protein trafficking (NUS1, PHS1, PGA2, PGA3), and we found that CSE1 and SMC4 are important for DNA replication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations in the gene encoding the 34 kDa subunit of yeast replication protein A cause defective S phase progression.J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 8;254(4):595-607. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0641. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7500336
-
CLN3 expression is sufficient to restore G1-to-S-phase progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants defective in translation initiation factor eIF4E.Biochem J. 1999 May 15;340 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):135-41. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10229668 Free PMC article.
-
Genome rearrangements caused by depletion of essential DNA replication proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2012 Sep;192(1):147-60. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.141051. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22673806 Free PMC article.
-
Start and the restriction point.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Dec;25(6):717-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23916770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring conditional gene essentiality through systems genetics approaches in yeast.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022 Oct;76:101963. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2022.101963. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022. PMID: 35939967 Review.
Cited by
-
SMC4 enhances the chemoresistance of hepatoma cells by promoting autophagy.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1308. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3623. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660610 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of Nogo-B receptor, a subunit of cis-prenyltransferase, causes a congenital disorder of glycosylation.Cell Metab. 2014 Sep 2;20(3):448-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.06.016. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cell Metab. 2014. PMID: 25066056 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of essential genes in Caenorhabditis elegans through whole-genome sequencing of legacy mutant collections.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Dec 8;11(12):jkab328. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab328. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 34550348 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting the level of the proteins essential for the regulation of the initiation step of replication extends the chronological lifespan and reproductive potential in budding yeast.Biogerontology. 2024 Oct;25(5):859-881. doi: 10.1007/s10522-024-10113-x. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 38844751 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of essential genes reveals important regulators of G protein signaling.Mol Cell. 2010 Jun 11;38(5):746-57. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.026. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20542006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angermayr M., Roidl A., Bandlow W. Yeast Rio1p is the founding member of a novel subfamily of protein serine kinases involved in the control of cell cycle progression. Mol. Microbiol. 2002;44:309–324. - PubMed
-
- Aono N., Sutani T., Tomonaga T., Mochida S., Yanagida M. Cnd2 has dual roles in mitotic condensation and interphase. Nature. 2002;417:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio O. M., Weinstein D. M., Bell S. P. Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: redistribution of MCM proteins and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell. 1997;91:59–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

