A survey of essential gene function in the yeast cell division cycle
- PMID: 16943325
- PMCID: PMC1635385
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-04-0368
A survey of essential gene function in the yeast cell division cycle
Abstract
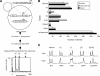
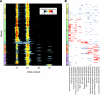
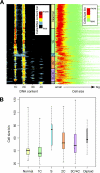
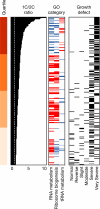
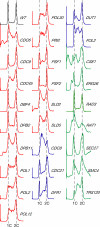
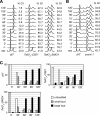
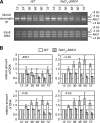
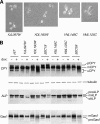
Mutations impacting specific stages of cell growth and division have provided a foundation for dissecting mechanisms that underlie cell cycle progression. We have undertaken an objective examination of the yeast cell cycle through flow cytometric analysis of DNA content in TetO(7) promoter mutant strains representing 75% of all essential yeast genes. More than 65% of the strains displayed specific alterations in DNA content, suggesting that reduced function of an essential gene in most cases impairs progression through a specific stage of the cell cycle. Because of the large number of essential genes required for protein biosynthesis, G1 accumulation was the most common phenotype observed in our analysis. In contrast, relatively few mutants displayed S-phase delay, and most of these were defective in genes required for DNA replication or nucleotide metabolism. G2 accumulation appeared to arise from a variety of defects. In addition to providing a global view of the diversity of essential cellular processes that influence cell cycle progression, these data also provided predictions regarding the functions of individual genes: we identified four new genes involved in protein trafficking (NUS1, PHS1, PGA2, PGA3), and we found that CSE1 and SMC4 are important for DNA replication.
Figures
References
-
- Angermayr M., Roidl A., Bandlow W. Yeast Rio1p is the founding member of a novel subfamily of protein serine kinases involved in the control of cell cycle progression. Mol. Microbiol. 2002;44:309–324. - PubMed
-
- Aono N., Sutani T., Tomonaga T., Mochida S., Yanagida M. Cnd2 has dual roles in mitotic condensation and interphase. Nature. 2002;417:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio O. M., Weinstein D. M., Bell S. P. Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: redistribution of MCM proteins and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell. 1997;91:59–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

