Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2X4 knock-out mice
- PMID: 16943557
- PMCID: PMC6675341
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2370-06.2006
Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2X4 knock-out mice
Abstract
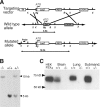
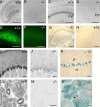
P2X4 purinergic receptors are calcium-permeable, ATP-activated ion channels. In the CA1 area of the hippocampus, they are located at the subsynaptic membrane somewhat peripherally to AMPA receptors. The possible role of P2X4 receptors has been difficult to elucidate because of the lack of selective antagonists. Here we report the generation of a P2X4 receptor knock-out mouse and show that long-term potentiation (LTP) at Schaffer collateral synapses is reduced relative to that in wild-type mice. Ivermectin, which selectively potentiates currents at P2X4, was found to increase LTP in wild-type mice but had no effect in P2X4 knock-out mice. We suggest that calcium entry through subsynaptic P2X4 receptors during high-frequency stimulation contributes to synaptic strengthening.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson WW, Collingridge GL. The LTP Program: a data acquisition program for on-line analysis of long-term potentiation and other synaptic events. J Neurosci Methods. 2001;108:71–83. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Conquet F. Inactivation in vivo of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 by specific chromosomal insertion of reporter gene lacZ. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34:865–870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
