Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein in the mitochondrial import channels of human Alzheimer's disease brain is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction
- PMID: 16943564
- PMCID: PMC6675337
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1469-06.2006
Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein in the mitochondrial import channels of human Alzheimer's disease brain is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction
Abstract
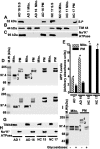
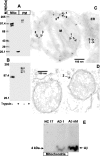
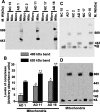
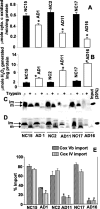
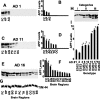
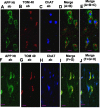
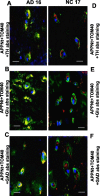
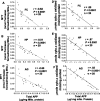
Mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the major intracellular lesions of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the causative factors involved in the mitochondrial dysfunction in human AD are not well understood. Here we report that nonglycosylated full-length and C-terminal truncated amyloid precursor protein (APP) accumulates exclusively in the protein import channels of mitochondria of human AD brains but not in age-matched controls. Furthermore, in AD brains, mitochondrially associated APP formed stable approximately 480 kDa complexes with the translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane 40 (TOM40) import channel and a super complex of approximately 620 kDa with both mitochondrial TOM40 and the translocase of the inner mitochondrial membrane 23 (TIM23) import channel TIM23 in an "N(in mitochondria)-C(out cytoplasm)" orientation. Accumulation of APP across mitochondrial import channels, which varied with the severity of AD, inhibited the entry of nuclear-encoded cytochrome c oxidase subunits IV and Vb proteins, which was associated with decreased cytochrome c oxidase activity and increased levels of H2O2. Regional distribution of mitochondrial APP showed higher levels in AD-vulnerable brain regions, such as the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala. Mitochondrial accumulation of APP was also observed in the cholinergic, dopaminergic, GABAergic, and glutamatergic neuronal types in the category III AD brains. The levels of translocationally arrested mitochondrial APP directly correlated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, apolipoprotein genotype analysis revealed that AD subjects with the E3/E4 alleles had the highest content of mitochondrial APP. Collectively, these results suggest that abnormal accumulation of APP across mitochondrial import channels, causing mitochondrial dysfunction, is a hallmark of human AD pathology.
Figures
References
-
- Agin V, Chichery R, Chichery M. Effects of learning on cytochrome oxidase activity in cuttlefish brain. NeuroReport. 2001;12:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Basun H, Forssell LG, Wetterberg L, Winblad B. Metals and trace elements in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect. 1991;3:231–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
