Special problems of pacing in children
- PMID: 16943987
- PMCID: PMC1555629
Special problems of pacing in children
Abstract
The number of children suffering from congenital or acquired rhythm disorders, and therefore being pacemaker dependent, is very small. This is one of the reasons why a special hardware has never been developed for this cohort. Pacemaker implantation into children does not differ substantially from operations in adults. But there are several important points which have to be fulfilled in these small patients in order to guarantee a complication free function. As most of these children remain pacemaker dependent a lifetime, it is of tremendous importance to minimize all revisions regarding the implanted systems and to enable our small patients a high and therefore nearly normal quality of life. Pros and cons of different surgical approaches, implantation sites and the problem of growth after pacemaker implantation in children are considered.
Figures
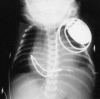
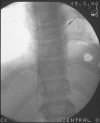
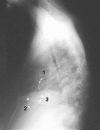
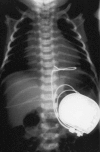
Similar articles
-
Biventricular pacing (cardiac resynchronization therapy): an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(13):1-60. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074464 Free PMC article.
-
Dual chamber cardiac pacing in children: Single chamber pacing dual chamber sensing cardiac pacemaker or dual chamber pacing and sensing cardiac pacemaker?Pediatr Int. 2002 Dec;44(6):635-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-200x.2002.01631.x. Pediatr Int. 2002. PMID: 12421261
-
[Left atrial and ventricular epicardial dual chamber pacing through a left lateral thoracotomy to treat pediatric complete atrioventricular block].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Aug;51(8):578-83. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24225287 Chinese.
-
Review of the epidemiology, pathogenesis and prevention of atrial fibrillation after pacemaker implantation.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jun;32(6):707-718. doi: 10.17219/acem/157239. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36881357 Review.
-
Pacing device therapy in infants and children: a review.J Artif Organs. 2013 Mar;16(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s10047-012-0668-y. Epub 2012 Oct 27. J Artif Organs. 2013. PMID: 23104398 Review.
Cited by
-
The psychological impact of permanent cardiac pacemakers on pediatric patients and their parents: A case control study.Indian Heart J. 2018 Nov-Dec;70(6):872-878. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Indian Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30580859 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical approaches to epicardial pacemaker placement: does pocket location affect lead survival?Pediatr Cardiol. 2010 Oct;31(7):1016-24. doi: 10.1007/s00246-010-9754-1. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Pediatr Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20690018 Free PMC article.
-
[Anaesthesia for cardiac catheterization in children].Anaesthesist. 2006 Dec;55(12):1291-8. doi: 10.1007/s00101-006-1105-5. Anaesthesist. 2006. PMID: 17077934 Review. German.
-
New Guidelines of Pediatric Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices: What Is Changing in Clinical Practice?J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Mar 27;11(4):99. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11040099. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 38667717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thoracic epidural infusion with chloroprocaine for postoperative analgesia following epicardial pacemaker placement in an infant.J Pain Res. 2014 Oct 23;7:609-13. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S73309. eCollection 2014. J Pain Res. 2014. PMID: 25364272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bink-Boelkens MTHE. Cardiac pacing in infants and children. Neth J Cardiol. 1992;5:199–202.
-
- Elmquist R, Senning A. An implantable pacemaker for the heart. In: Smyth CN, editor. Medical Electronics; Second International Conference; 1959; Paris. 1960.
-
- Bevilacqua L, Hordof A. Cardiac pacing in children. Curr Opin Cardiol. 1998;13:48–55. - PubMed
-
- Mann C, Antretter H, Hammerer I. Pacemaker therapy in a pediatric patient with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy and rapid intrinsic atrioventricular conduction. Pediatr Cardiol. 1999;20:229–231. - PubMed
-
- Rishi F, Hulse E, Auld DO, et al. Effects of dual-chamber pacing for pediatric patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. JACC. 1997;29:734–740. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
