A randomised controlled trial investigating the effect of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on cognitive and retinal function in cognitively healthy older people: the Older People And n-3 Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (OPAL) study protocol [ISRCTN72331636]
- PMID: 16945130
- PMCID: PMC1564406
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-5-20
A randomised controlled trial investigating the effect of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on cognitive and retinal function in cognitively healthy older people: the Older People And n-3 Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (OPAL) study protocol [ISRCTN72331636]
Abstract
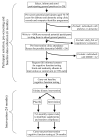
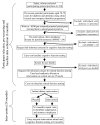
The number of individuals with age-related cognitive impairment is rising dramatically in the UK and globally. There is considerable interest in the general hypothesis that improving the diet of older people may slow the progression of cognitive decline. To date, there has been little attention given to the possible protective role of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 LCPs) most commonly found in oily fish, in age-related loss of cognitive function. The main research hypothesis of this study is that an increased dietary intake of n-3 LCPs will have a positive effect on cognitive performance in older people in the UK. To test this hypothesis, a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial will be carried out among adults aged 70-79 years in which the intervention arm will receive daily capsules containing n-3 LCP (0.5 g/day docosahexaenoic acid and 0.2 g/day eicosapentaenoic acid) while the placebo arm will receive daily capsules containing olive oil. The main outcome variable assessed at 24 months will be cognitive performance and a second major outcome variable will be retinal function. Retinal function tests are included as the retina is a specifically differentiated neural tissue and therefore represents an accessible window into the functioning of the brain. The overall purpose of this public-health research is to help define a simple and effective dietary intervention aimed at maintaining cognitive and retinal function in later life. This will be the first trial of its kind aiming to slow the decline of cognitive and retinal function in older people by increasing daily dietary intake of n-3 LCPs. The link between cognitive ability, visual function and quality of life among older people suggests that this novel line of research may have considerable public health importance.
Figures
References
-
- Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, Jorm A, Mathers C, Menezes PR, Rimmer E, Scazufca M. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet. 2005;366:2112–2117. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO/TUFTS . Keep fit for life: meeting the nutritional needs of older persons. Geneva , World Health Organisation; 2002.
-
- Uauy R, Hoffman DR, Peirano P, Birch DG, Birch EE. Essential fatty acids in visual and brain development. Lipids. 2001;36:885–895. - PubMed
-
- Soderberg M, Edlund C, Kristensson K, Dallner G. Lipid compositions of different regions of the human brain during aging. J Neurochem. 1990;54:415–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical