A mass spectrometry-based approach for identifying novel DNA polymerase substrates from a pool of dNTP analogues
- PMID: 16945949
- PMCID: PMC1636374
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl632
A mass spectrometry-based approach for identifying novel DNA polymerase substrates from a pool of dNTP analogues
Abstract
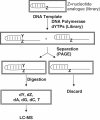
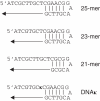
There has been a long-standing interest in the discovery of unnatural nucleotides that can be incorporated into DNA by polymerases. However, it is difficult to predict which nucleotide analogs will prove to have biological relevance. Therefore, we have developed a new screening method to identify novel substrates for DNA polymerases. This technique uses the polymerase itself to select a dNTP from a pool of potential substrates via incorporation onto a short oligonucleotide. The unnatural nucleotide(s) is then identified by high-resolution mass spectrometry. By using a DNA polymerase as a selection tool, only the biologically relevant members of a small nucleotide library can be quickly determined. We have demonstrated that this method can be used to discover unnatural base pairs in DNA with a detection threshold of < or =10% incorporation.
Figures



References
-
- Doublie S., Sawaya M.R., Ellenberger T. An open and closed case for all polymerases. Structure. 1999;7:R31–R35. - PubMed
-
- Jager J., Pata J.D. Getting a grip: polymerases and their substrate complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999;9:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Chiaramonte M., Moore C.L., Kincaid K., Kuchta R.D. Facile polymerization of dNTPs bearing unnatural base analogues by DNA polymerase alpha and Klenow fragment (DNA polymerase I) Biochemistry. 2003;42:10472–10481. - PubMed

