Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis
- PMID: 16945972
- PMCID: PMC1890411
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116632
Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis
Abstract
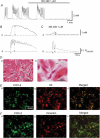
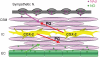
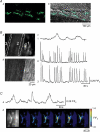
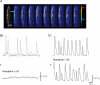
Smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and corporal tissue exhibit spontaneous contractile activity which depends on L-type Ca(2+) channels. The mechanism underlying this activity is spontaneous electrical activity which shows varied form and property between these tissues. Recent studies revealed that interstitial cells (ICs) are widely distributed in the genitourinary system, and suggested their involvement in spontaneous muscle activity. ICs in the system are not a simple analogy of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) in the gut, which act as electrical pacemaker, but represent variability amongst tissues which may account for individual characteristics of each organ. In the bladder and corporal tissue, where smooth muscle cells are capable of generating spontaneous electrical activity, ICs may modulate smooth muscle activity. ICs in corporal tissue release prostaglandins via cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) activity and reinforce not only spontaneous but also nerve-mediated alpha-adrenergic contractions. In the bladder, their fundamental role in the integration of signals between populations of cells has been proposed, and thus changes in ICs may contribute to an overactive bladder, a pathological condition which results from increased excitability in detrusor smooth muscles. In the urethra, ICs may act as electrical pacemakers as do ICC. However, overall contractility of urethral smooth muscles does not necessarily rely on pacemaking of ICs, and thus some population of smooth muscles may also have their own excitability.
Figures
References
-
- Azadzoi KM, Kim N, Brown ML, Goldstein I, Cohen RA, Saenz De Tejada I. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase products modulate corpus cavernosum smooth muscle tone. J Urol. 1992;147:220–225. - PubMed
-
- Biers SM, Reynard JM, Doore T, Brading AF. The functional effects of a c-kit tyrosine inhibitor on guinea-pig and human detrusor. BJU Int. 2006;97:612–616. - PubMed
-
- Bivalacqua TJ, Champion HC, Usta MF, Cellek S, Chitaley K, Webb RC, Lewis RL, Mills TM, Hellstrom WJ, Kadowitz PJ. RhoA/Rho-kinase suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the penis: a mechanism for diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:9121–9126. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brading AF. A myogenic basis for overactive bladder. Urology. 1997;50:57–67. - PubMed
-
- Brading AF, McCloskey KD. Mechanisms of disease: specialized interstitial cells of the urinary tract – an assessment of current knowledge. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005;2:546–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

