Minireview: rapid glucocorticoid signaling via membrane-associated receptors
- PMID: 16946006
- PMCID: PMC3280589
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2006-0981
Minireview: rapid glucocorticoid signaling via membrane-associated receptors
Abstract
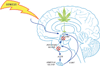
Glucocorticoids are secreted into the systemic circulation from the adrenal cortex and initiate a broad range of actions throughout the organism that regulate the function of multiple organ systems, including the liver, muscle, the immune system, the pancreas, fat tissue, and the brain. Delayed glucocorticoid effects are mediated by classical steroid mechanisms involving transcriptional regulation. Relatively rapid effects of glucocorticoids also occur that are incompatible with genomic regulation and invoke a noncanonical mode of steroid action. Studies conducted in several labs and on different species suggest that the rapid effects of glucocorticoids are mediated by the activation of one or more membrane-associated receptors. Here, we provide a brief review focused on multiple lines of evidence suggesting that rapid glucocorticoid actions are triggered by, or at least dependent on, membrane-associated G protein-coupled receptors and activation of downstream signaling cascades. We also discuss the possibility that membrane-initiated actions of glucocorticoids may provide an additional mechanism for the regulation of gene transcription.
Figures
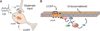
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of rapid glucocorticoid feedback inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.Stress. 2011 Jul;14(4):398-406. doi: 10.3109/10253890.2011.586446. Stress. 2011. PMID: 21663538 Free PMC article.
-
Fast glucocorticoid actions on brain: back to the future.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2005 Oct-Dec;26(3-4):103-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2005.08.001. Epub 2005 Oct 18. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16242180 Review.
-
Novel aspects of glucocorticoid actions.J Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Sep;26(9):557-72. doi: 10.1111/jne.12157. J Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24724595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reinterpretation of basal glucocorticoid feedback: implications to behavioral and metabolic disease.Vitam Horm. 2004;69:1-29. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(04)69001-7. Vitam Horm. 2004. PMID: 15196877 Review.
-
Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility.Stress. 2018 Sep;21(5):403-416. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2018.1470238. Epub 2018 May 15. Stress. 2018. PMID: 29764284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hair cortisol predicts object permanence performance in infant rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta).Dev Psychobiol. 2009 Dec;51(8):706-13. doi: 10.1002/dev.20405. Dev Psychobiol. 2009. PMID: 19771550 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and significance of nuclear receptor auto- and cross-regulation.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2011 Jan 1;170(1):3-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.03.013. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 20338175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid receptors are localized to dendritic spines and influence local actin signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Oct;46(2):304-15. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8288-3. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22717988 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids and Stress-Induced Changes in the Expression of PERIOD1 in the Rat Forebrain.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 15;10(6):e0130085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130085. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26075608 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted hypothalamic CRH neuron responsiveness contributes to diet-induced obesity.EMBO Rep. 2020 Jul 3;21(7):e49210. doi: 10.15252/embr.201949210. Epub 2020 May 27. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 32462726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keller-Wood ME, Dallman MF. Corticosteroid inhibition of ACTH secretion. Endocr Rev. 1984;5:1–24. - PubMed
-
- de Kloet ER. Stress in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;405:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Falkenstein E, Tillmann HC, Christ M, Feuring M, Wehling M. Multiple actions of steroid hormones: a focus on rapid, nongenomic effects. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:513–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

