Enhanced radiation sensitivity and radiation recall dermatitis (RRD) after hypericin therapy -- case report and review of literature
- PMID: 16948841
- PMCID: PMC1564402
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-1-32
Enhanced radiation sensitivity and radiation recall dermatitis (RRD) after hypericin therapy -- case report and review of literature
Abstract
Background: Modern radiotherapy (RT) reduces the side effects at organ at risk. However, skin toxicity is still a major problem in many entities, especially head and neck cancer. Some substances like chemotherapy provide a risk of increased side effects or can induce a "recall phenomenon" imitating acute RT-reactions months after RT. Moreover, some phototoxic drugs seem to enhance side effects of radiotherapy while others do not. We report a case of "radiation recall dermatitis" (RRD) one year after RT as a result of taking hypericin (St. John's wort).
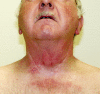
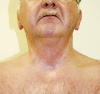
Case report: A 65 year old man with completely resected squamous cell carcinoma of the epiglottis received an adjuvant locoregional RT up to a dose of 64.8 Gy. The patient took hypericin during and months after RT without informing the physician. During radiotherapy the patient developed unusual intensive skin reactions. Five months after RT the skin was completely bland at the first follow up. However, half a year later the patient presented erythema, but only within the area of previously irradiated skin. After local application of a steroid cream the symptoms diminished but returned after the end of steroid therapy. The anamnesis disclosed that the patient took hypericin because of depressive mood. We recommended to discontinue hypericin and the symptoms disappeared afterward.
Conclusion: Several drugs are able to enhance skin toxicity of RT. Furthermore, the effect of RRD is well known especially for chemotherapy agents such as taxans. However, the underlying mechanisms are not known in detail so far. Moreover, it is unknown whether photosensitising drugs can also be considered to increase radiation sensitivity and whether a recall phenomenon is possible. The first report of a hypericin induced RRD and review of the literature are presented. In clinical practise many interactions between drugs and radiotherapy were not noticed and if registered not published. We recommend to ask especially for complementary or alternative drugs because patients tend to conceal such medication as harmless.
Figures

References
-
- Kuhnt T, Richter C, Enke H, Dunst J. Acute radiation reaction and local control in breast cancer patients treated with postmastectomy radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol. 1998;174:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Kuhnt T, Becker A, Pigorsch S, Pelz T, Bloching M, Passmann M, et al. Aggressive simultaneous radiochemotherapy with cisplatin and paclitaxel in combination with accelerated hyperfractionated radiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck tumors. Results of a phase I-II trial. Strahlenther Onkol. 2003;179:673–681. doi: 10.1007/s00066-003-1106-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schuck A, Biermann M, Pixberg MK, Muller SB, Heinecke A, Schober O, et al. Acute toxicity of adjuvant radiotherapy in locally advanced differentiated thyroid carcinoma. First results of the multicenter study differentiated thyroid carcinoma (MSDS) Strahlenther Onkol. 2003;179:832–839. doi: 10.1007/s00066-003-1158-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

