High tibial osteotomy with use of the Taylor Spatial Frame external fixator for osteoarthritis of the knee
- PMID: 16948882
- PMCID: PMC3207566
High tibial osteotomy with use of the Taylor Spatial Frame external fixator for osteoarthritis of the knee
Abstract
Background: High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is used to treat medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee in active patients with varus alignment. In this study we review the clinical and radiographic outcomes associated with the Taylor Spatial Frame (Smith & Nephew), and its use in HTOs, and we include an illustrative case report.
Methods: In 7 patients with medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee and varus alignment, the Taylor Spatial Frame was applied to the tibia in the operating room and a proximal tibial osteotomy was performed. Patients followed a computer-generated turning schedule until the desired correction was achieved. The frame was removed when the osteotomy site had healed. The lower extremity measure (LEM) was used to assess physical function. Clinical outcome measures relating to the Taylor Spatial Frame included latency, time to correction, time in the frame, number of residual corrections and complications. Radiographic outcomes included preoperative Resnick grades of osteoarthritis, pre- and post-correction limb alignment and tibial slope measurements.
Results: Average (and standard deviation) LEM grade at a mean 41 (14) months follow-up after correction was 94% (5%). Average latency was 8 days, time to correction was 15 days, time in the frame was 23 weeks and number of residual corrections was 1.3. Complications were similar to those for external fixators. Radiographic correction goals were met in all patients.
Conclusion: The Taylor Spatial Frame is a valuable asset when using HTO to treat medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee.
Contexte: On utilise l'ostéotomie tibiale haute (OTH) pour traiter une arthrose de la loge interne du genou chez les patients actifs qui ont un alignement en varus. Au cours de cette étude, nous analysons les résultats cliniques et radiographiques associés au cadre spatial de Taylor (Smith et Nephew) et l'utilisation qu'on en fait dans l'OTH, et nous incluons un rapport de cas comme exemple.
Méthodes: Chez sept patients atteints d'arthrose de la loge interne du genou et qui avaient un alignement en varus, on a mis en place le cadre spatial de Taylor sur le tibia à la salle d'opération et pratiqué une ostéotomie tibiale proximale. Les patients ont suivi un horaire de torsion produit par ordinateur jusqu'à ce que la correction souhaitée soit établie. On a enlevé le cadre une fois le site de l'ostéotomie guéri. On a utilisé la mesure du membre inférieur (MMI) pour évaluer la fonction physique. Les mesures des résultats cliniques reliés au cadre spatial de Taylor comprennent la latence, le temps nécessaire pour réaliser la correction, la durée d'application du cadre, le nombre de corrections résiduelles et les complications. Les résultats radiographiques comprennent les grades préopératoires de Resnick de l'arthrose, l'alignement du membre avant et après la correction et les mesures de la pente tibiale.
Résultats: La MMI moyenne (et l'écart type) à un suivi moyen de 41 (14) mois après la correction s'est établie à 94 % (5 %). La durée moyenne de la latence s'est établie à huit jours, le temps nécessaire pour réaliser la correction, à 15 jours, la durée de l'application du cadre, à 23 semaines, et le nombre de corrections résiduelles, à 1,3. Les complications étaient semblables à celles que causent les appareils de fixation externe. Les objectifs radiographiques de la correction ont été atteints chez tous les patients.
Conclusion: Le cadre spatial de Taylor se révèle avantageux lorsqu'on utilise l'OTH pour traiter une arthrose de la loge interne du genou.
Figures

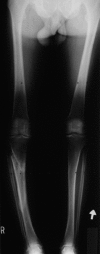
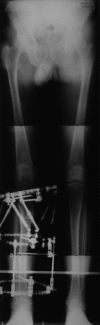
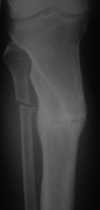
References
-
- Naudie D, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, et al. The Install Award. Survivorship of the high tibial valgus osteotomy. A 10- to 22-year followup study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;(367):18-27. - PubMed
-
- Billings A, Scott DF, Camargo MP, et al. High tibial osteotomy with a calibrated osteotomy guide, rigid internal fixation, and early motion. Long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82:70-9. - PubMed
-
- Berman AT, Bosacco SJ, Kirshner S, et al. Factors influencing long-term results in high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991;(272):192-8. - PubMed
-
- Aglietti P, Rinonapoli E, Stringa G, et al. Tibial osteotomy for the varus osteoarthritic knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983;(176):239-51. - PubMed
-
- Stukenborg-Colsman C, Wirth CJ, Lazovic D, et al. High tibial osteotomy versus unicompartmental joint replacement in unicompartmental knee joint osteoarthritis: 7–10-year follow-up prospective randomised study. Knee 2001;8:187-94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
