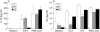IRAK4 and NEMO mutations in otherwise healthy children with recurrent invasive pneumococcal disease
- PMID: 16950813
- PMCID: PMC2597905
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2006.044446
IRAK4 and NEMO mutations in otherwise healthy children with recurrent invasive pneumococcal disease
Abstract
Background: About 2% of childhood episodes of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) are recurrent, and most remain unexplained.
Objective: To report two cases of otherwise healthy, unrelated children with recurrent IPD as the only clinical infectious manifestation of an inherited disorder in nuclear factor-kappaB(NF-kappaB)-dependent immunity.
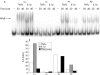
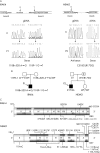
Results: One child carried two germline mutations in IRAK4, and had impaired cellular responses to interleukin (IL)1 receptor and toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation. The other child carried a hemizygous mutation in NEMO, associated with a broader impairment of NF-kappaB activation, with an impaired cellular response to IL-1R, TLR and tumour necrosis factor receptor stimulation. The two patients shared a narrow clinical phenotype, associated with two related but different genotypes.
Conclusions: Otherwise healthy children with recurrent IPD should be explored for underlying primary immunodeficiencies affecting the IRAK4-dependent and NEMO-dependent signalling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: XB is a senior clinical investigator of the Fund for Scientific Research—Flanders. J‐LC is an International Scholar of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Similar articles
-
Novel primary immunodeficiencies revealed by the investigation of paediatric infectious diseases.Curr Opin Immunol. 2008 Feb;20(1):39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.10.005. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18083507 Review.
-
Recurrent systemic pneumococcal disease in children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007 Jun;26(6):480-4. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31805ce277. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007. PMID: 17529863
-
Primary immunodeficiency to pneumococcal infection due to a defect in Toll-like receptor signaling.J Pediatr. 2004 Apr;144(4):512-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2003.10.034. J Pediatr. 2004. PMID: 15069402
-
Recurrent systemic pneumococcal disease and IRAK4 deficiency.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007 Nov;26(11):1074; author reply 1074. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318156fb93. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007. PMID: 17984826 No abstract available.
-
Heritable defects of the human TLR signalling pathways.J Endotoxin Res. 2005;11(4):220-4. doi: 10.1179/096805105X37367. J Endotoxin Res. 2005. PMID: 16176658 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent invasive pneumococcal disease in children: underlying clinical conditions, and immunological and microbiological characteristics.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 4;10(3):e0118848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118848. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25738983 Free PMC article.
-
IRAK-4 and MyD88 deficiencies impair IgM responses against T-independent bacterial antigens.Blood. 2014 Dec 4;124(24):3561-71. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-587824. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25320238 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The challenge of assessing infant vaccine responses in resource-poor settings.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010 Jun;9(6):665-74. doi: 10.1586/erv.10.41. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2010. PMID: 20518720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PP4R1 sub-unit of protein phosphatase PP4 is essential for inhibition of NF-κB by merkel polyomavirus small tumour antigen.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 11;8(15):25418-25432. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15836. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28445980 Free PMC article.
-
NEMO is a key component of NF-κB- and IRF-3-dependent TLR3-mediated immunity to herpes simplex virus.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Sep;128(3):610-7.e1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.04.059. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21722947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong W Y, Overturf G D, Powars D R. Infection caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children with sickle cell disease: epidemiology, immunologic mechanisms, prophylaxis, and vaccination. Clin Infect Dis 1992141124–1136. - PubMed
-
- Picard C, Puel A, Ku C L, Casanova J L. Primary immunodeficiencies associated with pneumococcal disease. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol 20033451–459. - PubMed
-
- Doffinger R, Smahi A, Bessia C, Geissmann F, Feinberg J, Durandy A, Bodemer C, Kenwrick S, Dupuis‐Girod S, Blanche S, Wood P, Rabia S H, Headon D J, Overbeek P A, Le Deist F, Holland S M, Belani K, Kumararatne D S, Fischer A, Shapiro R, Conley M E, Reimund E, Kalhoff H, Abinun M, Munnich A, Israel A, Courtois G, Casanova J L. X‐linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency is caused by impaired NF‐kappaB signaling. Nat Genet 200127277–285. - PubMed
-
- Picard C, Puel A, Bonnet M, Ku C L, Bustamante J, Yang K, Soudais C, Dupuis S, Feinberg J, Fieschi C, Elbim C, Hitchcock R, Lammas D, Davies G, Al‐Ghonaium A, Al‐Rayes H, Al‐Jumaah S, Al‐Hajjar S, Al‐Mohsen I Z, Frayha H H, Rucker R, Hawn T R, Aderem A, Tufenkeji H, Haraguchi S, Day N K, Good R A, Gougerot‐Pocidalo M A, Ozinsky A, Casanova J L. Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with IRAK‐4 deficiency. Science 20032992076–2079. - PubMed
-
- Puel A, Picard C, Ku C L, Smahi A, Casanova J L. Inherited disorders of NF‐kappaB‐mediated immunity in man. Curr Opin Immunol 20041634–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous