Characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase gene from cucumber required for trichoderma-conferred plant resistance
- PMID: 16950863
- PMCID: PMC1630744
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.082107
Characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase gene from cucumber required for trichoderma-conferred plant resistance
Abstract
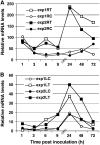
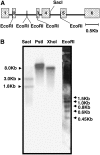
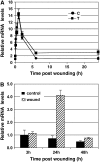
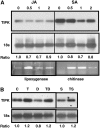
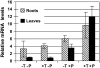
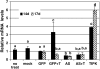
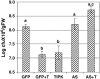
The fungal biocontrol agent Trichoderma asperellum has been recently shown to induce systemic resistance in plants through a mechanism that employs jasmonic acid and ethylene signal transduction pathways. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) proteins have been implicated in the signal transduction of a wide variety of plant stress responses. Here we report the identification and characterization of a Trichoderma-induced MAPK (TIPK) gene function in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Similar to its homologs, wound-induced protein kinase, MPK3, and MPK3a, TIPK is also induced by wounding. Normally, preinoculation of roots with Trichoderma activates plant defense mechanisms, which result in resistance to the leaf pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv lachrymans. We used a unique attenuated virus vector, Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV-AGII), to overexpress TIPK protein and antisense (AS) RNA. Plants overexpressing TIPK were more resistant to pathogenic bacterial attack than control plants, even in the absence of Trichoderma preinoculation. On the other hand, plants expressing TIPK-AS revealed increased sensitivity to pathogen attack. Moreover, Trichoderma preinoculation could not protect these AS plants against subsequent pathogen attack. We therefore demonstrate that Trichoderma exerts its protective effect on plants through activation of the TIPK gene, a MAPK that is involved in signal transduction pathways of defense responses.
Figures



References
-
- Abeles FB, Morgan PW, Saltveit ME Jr (1992) Ethylene in Plant Biology, Ed 2. Academic Press, San Diego
-
- Aly R, Mansour F, Abo Much F, Edelstein M, Gal-On A (2005) A novel approach to spider mite control based on expression of sarcotoxin IA peptide via ZYMV-AGII vector in squash plants. Phytoparasitica 33: 177–186
-
- Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415: 977–983 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

