Interplay between Ino80 and Swr1 chromatin remodeling enzymes regulates cell cycle checkpoint adaptation in response to DNA damage
- PMID: 16951256
- PMCID: PMC1560417
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1440206
Interplay between Ino80 and Swr1 chromatin remodeling enzymes regulates cell cycle checkpoint adaptation in response to DNA damage
Abstract
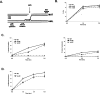
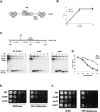
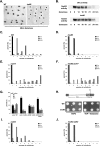
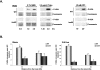
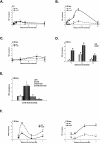
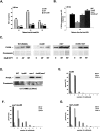
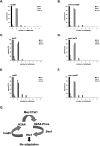
Ino80 and Swr1 are ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes that have been implicated in DNA repair. Here we show that Ino80 is required for cell cycle checkpoint adaptation in response to a persistent DNA double-strand break (DSB). The failure of cells lacking Ino80 to escape checkpoint arrest correlates with an inability to maintain high levels of histone H2AX phosphorylation and an increased incorporation of the Htz1p histone variant into chromatin surrounding the DSB. Inactivation of Swr1 eliminates this DNA damage-induced Htz1p incorporation and restores H2AX phosphorylation and checkpoint adaptation. We propose that Ino80 and Swr1 function antagonistically at chromatin surrounding a DSB, and that they regulate the incorporation of different histone H2A variants that can either promote or block cell cycle checkpoint adaptation.
Figures
References
-
- Bird A.W., Yu D.Y., Pray-Grant M.G., Qiu Q., Harmon K.E., Megee P.C., Grant P.A., Smith M.M., Christman M.F. Acetylation of histone H4 by Esa1 is required for DNA double-strand break repair. Nature. 2002;419:411–415. - PubMed
-
- Celeste A., Fernandez-Capetillo O., Kruhlak M.J., Pilch D.R., Staudt D.W., Lee A., Bonner R.F., Bonner W.M., Nussenzweig A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation is dispensable for the initial recognition of DNA breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003b;5:675–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
