Targeting chromosomal sites with locked nucleic acid-modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides: study of efficiency dependence on DNA nuclear environment
- PMID: 16951289
- PMCID: PMC1636373
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl630
Targeting chromosomal sites with locked nucleic acid-modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides: study of efficiency dependence on DNA nuclear environment
Abstract
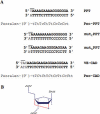
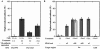
Triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) are synthetic DNA code-reading molecules that have been demonstrated to function to some extent in chromatin within cell nuclei. Here we have investigated the impact of DNA nuclear environment on the efficiency of TFO binding. For this study we have used locked nucleic acid-containing TFOs (TFO/LNAs) and we report the development of a rapid PCR-based method to quantify triplex formation. We have first compared triplex formation on genes located at different genomic sites and containing the same oligopyrimidine*oligopurine sequence. We have shown that efficient TFO binding is possible on both types of genes, expressed and silent. Then we have further investigated when gene transcription may influence triplex formation in chromatin. We have identified situations where for a given gene, increase of transcriptional activity leads to enhanced TFO binding: this was observed for silent or weakly expressed genes that are not or are only slightly accessible to TFO. Such a transcriptional dependence was observed for integrated and endogenous loci, and chemical and biological activations of transcription. Finally, we provide evidence that TFO binding is sequence-specific as measured on mutated target sequences and that up to 50% of chromosomal targets can be covered by the TFO/LNA in living cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intercalator conjugates of pyrimidine locked nucleic acid-modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides: improving DNA binding properties and reaching cellular activities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 27;33(13):4223-34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki726. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16049028 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and quantification of triple helix formation in chromosomal DNA.J Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 20;341(4):979-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.079. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15328613
-
Exploring cellular activity of locked nucleic acid-modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides and defining its molecular basis.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 20;280(20):20076-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500021200. Epub 2005 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15760901
-
Targeting DNA with triplex-forming oligonucleotides to modify gene sequence.Biochimie. 2008 Aug;90(8):1109-16. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.04.004. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Biochimie. 2008. PMID: 18460344 Review.
-
The development of bioactive triple helix-forming oligonucleotides.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Nov;1058:119-27. doi: 10.1196/annals.1359.020. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16394131 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioconjugation of oligonucleotides for treating liver fibrosis.Oligonucleotides. 2007 Winter;17(4):349-404. doi: 10.1089/oli.2007.0097. Oligonucleotides. 2007. PMID: 18154454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The triple helix: 50 years later, the outcome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Sep;36(16):5123-38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn493. Epub 2008 Aug 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18676453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locked nucleic acid oligomers as handles for single molecule manipulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct 29;42(19):e150. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku760. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25159617 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular antisense activity of peptide nucleic acid (PNAs) targeted to HIV-1 polypurine tract (PPT) containing RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):3907-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm374. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537815 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous recombination assay for interstrand cross-link repair.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;745:283-91. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-129-1_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21660700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Besch R., Giovannangeli C., Degitz K. Triplex-forming oligonucleotides—sequence-specific DNA ligands as tools for gene inhibition and for modulation of DNA-associated functions. Curr. Drug. Targets. 2004;5:691–703. - PubMed
-
- Rogers F.A., Lloyd J.A., Glazer P.M. Triplex-forming oligonucleotides as potential tools for modulation of gene expression. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:319–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

