Studies on the activity of the hypoxia-inducible-factor hydroxylases using an oxygen consumption assay
- PMID: 16952279
- PMCID: PMC1698668
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061151
Studies on the activity of the hypoxia-inducible-factor hydroxylases using an oxygen consumption assay
Abstract
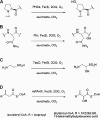
The activity and levels of the metazoan HIF (hypoxia-inducible factor) are regulated by its hydroxylation, catalysed by 2OG (2-oxoglutarate)- and Fe(II)-dependent dioxygenases. An oxygen consumption assay was developed and used to study the relationship between HIF hydroxylase activity and oxygen concentration for recombinant forms of two human HIF hydroxylases, PHD2 (prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 2) and FIH (factor inhibiting HIF), and compared with two other 2OG-dependent dioxygenases. Although there are caveats on the absolute values, the apparent K(m) (oxygen) values for PHD2 and FIH were within the range observed for other 2OG oxygenases. Recombinant protein substrates were found to have lower apparent K(m) (oxygen) values compared with shorter synthetic peptides of HIF. The analyses also suggest that human PHD2 is selective for fragments of the C-terminal over the N-terminal oxygen-dependent degradation domain of HIF-1alpha. The present results, albeit obtained under non-physiological conditions, imply that the apparent K(m) (oxygen) values of the HIF hydroxylases enable them to act as oxygen sensors providing their in vivo capacity is appropriately matched to a hydroxylation-sensitive signalling pathway.
Figures

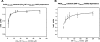
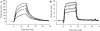

References
-
- Schofield C. J., Ratcliffe P. J. Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:343–354. - PubMed
-
- Semenza G. L. Hydroxylation of HIF-1: oxygen sensing at the molecular level. Physiology. 2004;19:176–182. - PubMed
-
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. Purification and characterization of hypoxia- inducible factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:1230–1237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

