Characterization of Stg fimbriae from an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O78:K80 strain and assessment of their contribution to colonization of the chicken respiratory tract
- PMID: 16952934
- PMCID: PMC1595498
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00453-06
Characterization of Stg fimbriae from an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O78:K80 strain and assessment of their contribution to colonization of the chicken respiratory tract
Abstract
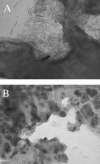
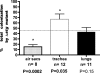
In a previous study, ecs-3, a sequence from avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) O78:K80 strain chi7122, was found to be expressed in vivo in infected chicken tissues. The region encompassing ecs-3 carries a fimbrial gene cluster that is a putative ortholog of the stg fimbrial gene cluster of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. This APEC fimbrial gene cluster, which we have termed stg, is a member of a distinct group of related fimbriae that are located in the glmS-pstS intergenic region of certain E. coli and S. enterica strains. Under the control of the pBAD promoter, the production of Stg fimbriae was demonstrated by Western blotting and immunogold electron microscopy with E. coli K-12. Transcriptional fusions suggest that stg expression is influenced by the carbohydrate source and decreased by the addition of iron and that Fur plays a role in the regulation of stg expression. stg sequences were associated with APEC O78 isolates, and stg was phylogenetically distributed among E. coli reference strains and clinical isolates from human urinary tract infections. Stg fimbriae contributed to the adherence of a nonfimbriated E. coli K-12 strain to avian lung sections and human epithelial cells in vitro. Coinfection experiments with APEC strain chi7122 and an isogenic Deltastg mutant demonstrated that compared to the wild-type parent, the Deltastg mutant was less able to colonize air sacs, equally able to colonize lungs, and able to more effectively colonize tracheas of infected chickens. Stg fimbriae, together with other adhesins, may therefore contribute to the colonization of avian respiratory tissues by certain APEC strains.
Figures




References
-
- Andrews, S. C., A. K. Robinson, and F. Rodriguez-Quinones. 2003. Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27:215-237. - PubMed
-
- Arné, P., D. Marc, A. Brée, C. Schouler, and M. Dho-Moulin. 2000. Increased tracheal colonization in chickens without impairing pathogenic properties of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli MT78 with a fimH deletion. Avian Dis. 44:343-355. - PubMed
-
- Babai, R., G. Blum-Oehler, B. E. Stern, J. Hacker, and E. Z. Ron. 1997. Virulence patterns from septicemic Escherichia coli O78 strains. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 149:99-105. - PubMed
-
- Bahrani-Mougeot, F. K., E. L. Buckles, C. V. Lockatell, J. R. Hebel, D. E. Johnson, C. M. Tang, and M. S. Donnenberg. 2002. Type 1 fimbriae and extracellular polysaccharides are preeminent uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence determinants in the murine urinary tract. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1079-1093. - PubMed
-
- Bäumler, A. J., A. J. Gilde, R. M. Tsolis, A. W. van der Velden, B. M. Ahmer, and F. Heffron. 1997. Contribution of horizontal gene transfer and deletion events to development of distinctive patterns of fimbrial operons during evolution of Salmonella serotypes. J. Bacteriol. 179:317-322. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

