Characterization of ferric and ferrous iron transport systems in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 16952942
- PMCID: PMC1595488
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00626-06
Characterization of ferric and ferrous iron transport systems in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
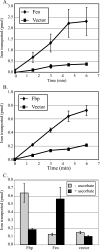
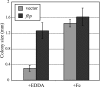
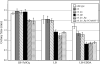
Vibrio cholerae has multiple iron acquisition systems, including TonB-dependent transport of heme and of the catechol siderophore vibriobactin. Strains defective in both of these systems grow well in laboratory media and in the infant mouse intestine, indicating the presence of additional iron acquisition systems. Previously uncharacterized potential iron transport systems, including a homologue of the ferrous transporter Feo and a periplasmic binding protein-dependent ATP binding cassette (ABC) transport system, termed Fbp, were identified in the V. cholerae genome sequence. Clones encoding either the Feo or the Fbp system exhibited characteristics of iron transporters: both repressed the expression of lacZ cloned under the control of a Fur-regulated promoter in Escherichia coli and also conferred growth on a Shigella flexneri mutant that has a severe defect in iron transport. Two other ABC transporters were also evaluated but were negative by these assays. Transport of radioactive iron by the Feo system into the S. flexneri iron transport mutant was stimulated by the reducing agent ascorbate, consistent with Feo functioning as a ferrous transporter. Conversely, ascorbate inhibited transport by the Fbp system, suggesting that it transports ferric iron. The growth of V. cholerae strains carrying mutations in one or more of the potential iron transport genes indicated that both Feo and Fbp contribute to iron acquisition. However, a mutant defective in the vibriobactin, Fbp, and Feo systems was not attenuated in a suckling mouse model, suggesting that at least one other iron transport system can be used in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vibrio cholerae VciB promotes iron uptake via ferrous iron transporters.J Bacteriol. 2008 Sep;190(17):5953-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.00569-08. Epub 2008 Jun 27. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18586940 Free PMC article.
-
Iron acquisition in Vibrio cholerae.Biometals. 2007 Jun;20(3-4):405-16. doi: 10.1007/s10534-006-9073-4. Epub 2007 Jan 10. Biometals. 2007. PMID: 17216354 Review.
-
The Vibrio cholerae VctPDGC system transports catechol siderophores and a siderophore-free iron ligand.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Sep;81(6):1446-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07775.x. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21790806 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae VciB Mediates Iron Reduction.J Bacteriol. 2017 May 25;199(12):e00874-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00874-16. Print 2017 Jun 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28348025 Free PMC article.
-
[Component and functional mechanism of the ferrous iron acquisition system in gram-negative bacteria - A review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016 Jul 4;56(7):1061-9. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 29732873 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Iron-Utilization System in Vibrio vulnificus M2799.Mar Drugs. 2021 Dec 17;19(12):710. doi: 10.3390/md19120710. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34940709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catechol Siderophore Transport by Vibrio cholerae.J Bacteriol. 2015 Sep;197(17):2840-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00417-15. Epub 2015 Jun 22. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26100039 Free PMC article.
-
The Yfe and Feo transporters are involved in microaerobic growth and virulence of Yersinia pestis in bubonic plague.Infect Immun. 2012 Nov;80(11):3880-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00086-12. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22927049 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae VciB promotes iron uptake via ferrous iron transporters.J Bacteriol. 2008 Sep;190(17):5953-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.00569-08. Epub 2008 Jun 27. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18586940 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental reservoirs and mechanisms of persistence of Vibrio cholerae.Front Microbiol. 2013 Dec 16;4:375. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00375. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24379807 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexeev, D., H. Zhu, M. Guo, W. Zhong, D. J. Hunter, W. Yang, D. J. Campopiano, and P. J. Sadler. 2003. A novel protein-mineral interface. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10:297-302. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Bagg, A., and J. B. Neilands. 1987. Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 26:5471-5477. - PubMed
-
- Bearden, S. W., and R. D. Perry. 1999. The Yfe system of Yersinia pestis transports iron and manganese and is required for full virulence of plague. Mol. Microbiol. 32:403-414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

