DsdX is the second D-serine transporter in uropathogenic Escherichia coli clinical isolate CFT073
- PMID: 16952954
- PMCID: PMC1595467
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00634-06
DsdX is the second D-serine transporter in uropathogenic Escherichia coli clinical isolate CFT073
Abstract
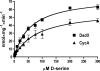
d-Serine is an amino acid present in mammalian urine that is inhibitory to Escherichia coli strains lacking a functional dsdA gene. Counterintuitively, a dsdA strain of E. coli clinical isolate CFT073 hypercolonizes the bladder and kidneys of mice relative to wild type during a coinfection in the murine model of urinary tract infection. We are interested in the mechanisms for uptake of d-serine in CFT073. d-Serine enters E. coli K-12 via CycA, the d-alanine transporter and d-cycloserine sensitivity locus. CFT073 cycA can grow on minimal medium with d-serine as a sole carbon source. The dsdX gene of the dsdCXA locus is a likely candidate for an additional d-serine transporter based on its predicted amino acid sequence similarity to gluconate transporters. In minimal medium, CFT073 dsdX can grow on d-serine as a sole carbon source; however, CFT073 dsdX cycA cannot. Additionally, CFT073 dsdXA cycA is not sensitive to inhibitory concentrations of d-serine during growth on glycerol and d-serine minimal medium. d-[(14)C]serine uptake experiments with CFT073 dsdX cycA harboring dsdX or cycA recombinant plasmids confirm that d-serine is able to enter E. coli cells via CycA or DsdX. In whole-cell d-[(14)C]serine uptake experiments, DsdX has an apparent K(m) of 58.75 microM and a V(max) of 75.96 nmol/min/mg, and CycA has an apparent K(m) of 82.40 microM and a V(max) of 58.90 nmol/min/mg. Only d-threonine marginally inhibits DsdX-mediated d-serine transport, whereas d-alanine, glycine, and d-cycloserine inhibit CycA-mediated d-serine transport. DsdX or CycA is sufficient to transport physiological quantities of d-serine, but DsdX is a d-serine-specific permease.
Figures
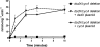
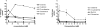
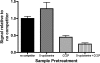
References
-
- Blomfield, I. C., M. S. McClain, and B. I. Eisenstein. 1991. Type 1 fimbriae mutants of Escherichia coli K12: characterization of recognized afimbriate strains and construction of new fim deletion mutants. Mol. Microbiol. 5:1439-1445. - PubMed
-
- Daley, D. O., M. Rapp, E. Granseth, K. Melen, D. Drew, and G. von Heijne. 2005. Global topology analysis of the Escherichia coli inner membrane proteome. Science 308:1321-1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

