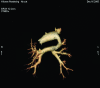
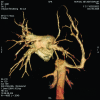
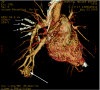
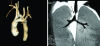Three-dimensional CT scanning: a new diagnostic modality in congenital heart disease
- PMID: 16952967
- PMCID: PMC1994429
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2006.101352
Three-dimensional CT scanning: a new diagnostic modality in congenital heart disease
Abstract
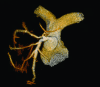
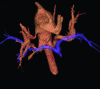
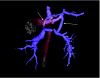
New generation multislice CT technology has changed the approach to non-invasive assessment of congenital heart disease, in both paediatric and adult patients. This is mainly because of rapid advances in spatial and temporal resolution and in post-processing capability. At Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, CT with multiplanar and three-dimensional reconstruction has become a routine examination in the evaluation of congenital heart disease planning surgery, complex interventional catheterisations and for follow-up. It has proved to be an invaluable diagnostic and decision-aiding methodology in these situations, as a complement to echocardiography and, increasingly, as a substitute for diagnostic angiography (which is usually associated with higher-dose radiation and longer sedation times, as well as occasional morbidity). This review illustrates the current status of 64-slice CT in congenital heart diseases, including assessment of the aorta, the coronary arteries, the pulmonary arteries, the systemic and pulmonary veins, and other intra- and extracardiac malformations.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared
References
-
- Schoenhagen P, Halliburton S S, Stillman A E.et al Noninvasive imaging of coronary arteries: current and future role of multi‐detector row CT. Radiology 20042327–17. - PubMed
-
- Pugliese F, Mollet N R, Runza G.et al Diagnostic accuracy of non‐invasive 64‐slice CT coronary angiography in patients with stable angina pectoris. Eur Radiol 2005161–8. - PubMed
-
- Quiroz R, Kucher N, Zou K H.et al Clinical validity of a negative computed tomography scan in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. JAMA 20052932012–2017. - PubMed
-
- Kapustin A J, Litt H I. Diagnostic imaging for aortic dissection. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 200517214–223. - PubMed