Foxo transcription factors blunt cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting calcineurin signaling
- PMID: 16952979
- PMCID: PMC4118290
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.637124
Foxo transcription factors blunt cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting calcineurin signaling
Abstract
Background: Cellular hypertrophy requires coordinated regulation of progrowth and antigrowth mechanisms. In cultured neonatal cardiomyocytes, Foxo transcription factors trigger an atrophy-related gene program that counters hypertrophic growth. However, downstream molecular events are not yet well defined.
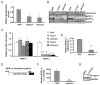
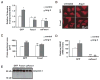
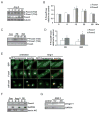
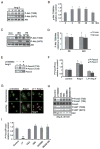
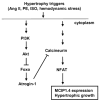
Methods and results: Here, we report that expression of either Foxo1 or Foxo3 in cardiomyocytes attenuates calcineurin phosphatase activity and inhibits agonist-induced hypertrophic growth. Consistent with these results, Foxo proteins decrease calcineurin phosphatase activity and repress both basal and hypertrophic agonist-induced expression of MCIP1.4, a direct downstream target of the calcineurin/NFAT pathway. Furthermore, hearts from Foxo3-null mice exhibit increased MCIP1.4 abundance and a hypertrophic phenotype with normal systolic function at baseline. Together, these results suggest that Foxo proteins repress cardiac growth at least in part through inhibition of the calcineurin/NFAT pathway. Given that hypertrophic growth of the heart occurs in multiple contexts, our findings also suggest that certain hypertrophic signals are capable of overriding the antigrowth program induced by Foxo. Consistent with this, multiple hypertrophic agonists triggered inactivation of Foxo proteins in cardiomyocytes through a mechanism requiring the PI3K/Akt pathway. In addition, both Foxo1 and Foxo3 are phosphorylated and consequently inactivated in hearts undergoing hypertrophic growth induced by hemodynamic stress.
Conclusions: This study suggests that inhibition of the calcineurin/NFAT signaling cascade by Foxo and release of this repressive action by the PI3K/Akt pathway are important mechanisms whereby Foxo factors govern cell growth in the heart.
Figures
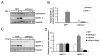

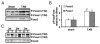
References
-
- Accili D, Arden KC. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell. 2004;117:421–426. - PubMed
-
- Tran H, Brunet A, Griffith EC, Greenberg ME. The many forks in FOXO’s road. Sci STKE. 2003:RE5. - PubMed
-
- Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, Panaro F, Timofeyva Y, Kline WO, Gonzalez M, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ. The IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription factors. Mol Cell. 2004;14:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Frey N, Katus HA, Olson EN, Hill JA. Hypertrophy of the heart: a new therapeutic target? Circulation. 2004;109:1580–1589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

