Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers are predominant DNA lesions in whole human skin exposed to UVA radiation
- PMID: 16954188
- PMCID: PMC1564232
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604213103
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers are predominant DNA lesions in whole human skin exposed to UVA radiation
Abstract
Solar UV radiation is the most important environmental factor involved in the pathogenesis of skin cancers. The well known genotoxic properties of UVB radiation (290-320 nm) mostly involve bipyrimidine DNA photoproducts. In contrast, the contribution of more-abundant UVA radiation (320-400 nm) that are not directly absorbed by DNA remains poorly understood in skin. Using a highly accurate and quantitative assay based on HPLC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry, we determined the type and the yield of formation of DNA damage in whole human skin exposed to UVB or UVA. Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, a typical UVB-induced DNA damage, were found to be produced in significant yield also in whole human skin exposed to UVA through a mechanism different from that triggered by UVB. Moreover, the latter class of photoproducts is produced in a larger amount than 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine, the most common oxidatively generated lesion, in human skin. Strikingly, the rate of removal of UVA-generated cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers was lower than those produced by UVB irradiation of skin. Finally, we compared the formation yields of DNA damage in whole skin with those determined in primary cultures of keratinocytes isolated from the same donors. We thus showed that human skin efficiently protects against UVB-induced DNA lesions, whereas very weak protection is afforded against UVA. These observations emphasize the likely role played by the UVA-induced DNA damage in skin carcinogenesis and should have consequences for photoprotection strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
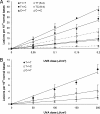
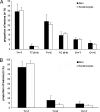
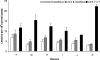
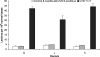
Comment in
-
Revisiting the photochemistry of solar UVA in human skin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Sep 12;103(37):13567-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605833103. Epub 2006 Sep 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16954200 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Larger yield of cyclobutane dimers than 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine in the DNA of UVA-irradiated human skin cells.Mutat Res. 2004 Nov 22;556(1-2):135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.07.011. Mutat Res. 2004. PMID: 15491641
-
Bipyrimidine photoproducts rather than oxidative lesions are the main type of DNA damage involved in the genotoxic effect of solar UVA radiation.Biochemistry. 2003 Aug 5;42(30):9221-6. doi: 10.1021/bi034593c. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12885257
-
Repair of the three main types of bipyrimidine DNA photoproducts in human keratinocytes exposed to UVB and UVA radiations.DNA Repair (Amst). 2005 Jul 12;4(7):836-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.05.001. DNA Repair (Amst). 2005. PMID: 15950551
-
Ultraviolet radiation-mediated damage to cellular DNA.Mutat Res. 2005 Apr 1;571(1-2):3-17. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.09.012. Epub 2005 Jan 26. Mutat Res. 2005. PMID: 15748634 Review.
-
Sunscreens containing the broad-spectrum UVA absorber, Mexoryl SX, prevent the cutaneous detrimental effects of UV exposure: a review of clinical study results.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008 Aug;24(4):164-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2008.00365.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008. PMID: 18717957 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro evaluation of sunscreens: an update for the clinicians.ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:352135. doi: 10.5402/2012/352135. Epub 2012 Nov 27. ISRN Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 23227355 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage and Deficiencies in the Mechanisms of Its Repair: Implications in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Immunol Res. 2018 Jul 12;2018:8214379. doi: 10.1155/2018/8214379. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30116756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of pyrrolopyrimidine derivatives on cancer cells cultured in vitro and potential mechanism.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 May;397(5):3169-3177. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02799-6. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37891256
-
Blue-violet laser modification of titania treated titanium: antibacterial and osteo-inductive effects.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 17;8(12):e84327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084327. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24358355 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin E inhibits the UVAI induction of "light" and "dark" cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, and oxidatively generated DNA damage, in keratinocytes.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 11;8(1):423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18924-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29323251 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

