A synthetic congener modeled on a microbicidal domain of thrombin- induced platelet microbicidal protein 1 recapitulates staphylocidal mechanisms of the native molecule
- PMID: 16954324
- PMCID: PMC1635186
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00038-06
A synthetic congener modeled on a microbicidal domain of thrombin- induced platelet microbicidal protein 1 recapitulates staphylocidal mechanisms of the native molecule
Abstract
Thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein 1 (tPMP-1) is a staphylocidal peptide released by activated platelets. This peptide initiates its microbicidal activity by membrane permeabilization, with ensuing inhibition of intracellular macromolecular synthesis. RP-1 is a synthetic congener modeled on the C-terminal microbicidal alpha-helix of tPMP-1. This study compared the staphylocidal mechanisms of RP-1 with those of tPMP-1, focusing on isogenic tPMP-1-susceptible (ISP479C) and -resistant (ISP479R) Staphylococcus aureus strains for the following quantitative evaluations: staphylocidal efficacy; comparative MIC; membrane permeabilization (MP) and depolarization; and DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. Although the proteins had similar MICs, RP-1 caused significant killing of ISP479C (<50% survival), correlating with extensive MP (>95%) and inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis (>90%), versus substantially reduced killing of ISP479R (>80% survival), with less MP (55%) and less inhibition of DNA or RNA synthesis (70 to 80%). Interestingly, RP-1-induced protein synthesis inhibition was equivalent in both strains. RP-1 did not depolarize the cell membrane and caused a relatively short postexposure growth inhibition. These data closely parallel those previously reported for tPMP-1 against this strain set and exemplify how synthetic molecules can be engineered to reflect structure-activity relationships of functional domains in native host defense effector molecules.
Figures
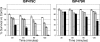
 ), or 100 (
), or 100 ( ) μg/ml of RP-1 or 2 μg/ml (▪) of tPMP-1. The mean percentage (±SD) of S. aureus survival versus controls was calculated from at least three independent experiments.
) μg/ml of RP-1 or 2 μg/ml (▪) of tPMP-1. The mean percentage (±SD) of S. aureus survival versus controls was calculated from at least three independent experiments.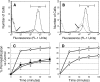
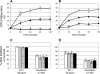
 , 90 min; and ▪, 120 min). Novobiocin was used as a positive control DNA synthesis inhibitor.
, 90 min; and ▪, 120 min). Novobiocin was used as a positive control DNA synthesis inhibitor.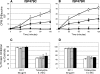
 , 90 min; and ▪, 120 min). Tetracycline was used as a positive control protein synthesis inhibitor.
, 90 min; and ▪, 120 min). Tetracycline was used as a positive control protein synthesis inhibitor.Similar articles
-
Inhibition of intracellular macromolecular synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus by thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal proteins.J Infect Dis. 2002 Feb 1;185(3):348-56. doi: 10.1086/338514. Epub 2002 Jan 17. J Infect Dis. 2002. PMID: 11807717
-
In vitro antibacterial activities of platelet microbicidal protein and neutrophil defensin against Staphylococcus aureus are influenced by antibiotics differing in mechanism of action.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 May;43(5):1111-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.5.1111. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 10223922 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet microbicidal proteins and neutrophil defensin disrupt the Staphylococcus aureus cytoplasmic membrane by distinct mechanisms of action.J Clin Invest. 1998 Jan 1;101(1):178-87. doi: 10.1172/JCI562. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9421480 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity in antistaphylococcal mechanisms among membrane-targeting antimicrobial peptides.Infect Immun. 2001 Aug;69(8):4916-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4916-4922.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11447168 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal resistance to antimicrobial peptides of mammalian and bacterial origin.Peptides. 2001 Oct;22(10):1651-9. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00500-9. Peptides. 2001. PMID: 11587793 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the LytSR two-component regulatory system in adaptation to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Aug;57(8):3875-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00412-13. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23733465 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific mutation of the sensor kinase GraS in Staphylococcus aureus alters the adaptive response to distinct cationic antimicrobial peptides.Infect Immun. 2014 Dec;82(12):5336-45. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02480-14. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25287929 Free PMC article.
-
Failures in clinical treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infection with daptomycin are associated with alterations in surface charge, membrane phospholipid asymmetry, and drug binding.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Jan;52(1):269-78. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00719-07. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 17954690 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus two-component regulatory system, GraRS, senses and confers resistance to selected cationic antimicrobial peptides.Infect Immun. 2012 Jan;80(1):74-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05669-11. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 21986630 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides and proteins with antimicrobial activity.Indian J Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;40(1):3-9. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.40481. Indian J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 21264153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayer, A. S., P. McNamara, M. R. Yeaman, N. Lucindo, T. Jones, A. L. Cheung, H.-G. Sahl, and R. A. Proctor. 2006. Transposon disruption of the complex I NADH oxidoreductase gene (snoD) in Staphylococcus aureus is associated with reduced susceptibility to the microbicidal activity of thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein 1. J. Bacteriol. 188:211-222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dhawan, V. K., M. R. Yeaman, and A. S. Bayer. 1990. Influence of in vitro susceptibility phenotype against thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein on treatment and prophylaxis outcomes of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J. Infect. Dis. 180:1561-1568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

