Rapid loss of intestinal crypts upon conditional deletion of the Wnt/Tcf-4 target gene c-Myc
- PMID: 16954380
- PMCID: PMC1636776
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00821-06
Rapid loss of intestinal crypts upon conditional deletion of the Wnt/Tcf-4 target gene c-Myc
Erratum in
-
Correction for Muncan et al., "Rapid Loss of Intestinal Crypts upon Conditional Deletion of the Wnt/Tcf-4 Target Gene c-Myc".Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Nov 28;38(24):e00482-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00482-18. Print 2018 Dec 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30487210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
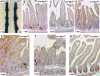
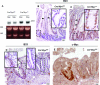
Inhibition of the mutationally activated Wnt cascade in colorectal cancer cell lines induces a rapid G1 arrest and subsequent differentiation. This arrest can be overcome by maintaining expression of a single Tcf4 target gene, the proto-oncogene c-Myc. Since colorectal cancer cells share many molecular characteristics with proliferative crypt progenitors, we have assessed the physiological role of c-Myc in adult crypts by conditional gene deletion. c-Myc-deficient crypts are lost within weeks and replaced by c-Myc-proficient crypts through a fission process of crypts that have escaped gene deletion. Although c-Myc(-/-) crypt cells remain in the cell cycle, they are on average much smaller than wild-type cells, cycle slower, and divide at a smaller cell size. c-Myc appears essential for crypt progenitor cells to provide the necessary biosynthetic capacity to successfully progress through the cell cycle.
Figures




References
-
- Arabi, A., S. Wu, K. Ridderstrale, H. Bierhoff, C. Shine, K. Fatyoul, S. Fahlen, P. Hydbring, O. Soderberg, I. Grummt, L. G. Larson, and A. P. Write. 2005. c-Myc associates with ribosomal DNA and activates RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:303-310. - PubMed
-
- Booth, D., and C. S. Potten. 2001. Protection against mucosal injury by growth factors and cytokines. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 29:16-20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
