Expression of the human germinal center-associated lymphoma (HGAL) protein identifies a subset of classic Hodgkin lymphoma of germinal center derivation and improved survival
- PMID: 16954503
- PMCID: PMC1785075
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-014977
Expression of the human germinal center-associated lymphoma (HGAL) protein identifies a subset of classic Hodgkin lymphoma of germinal center derivation and improved survival
Abstract
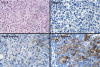
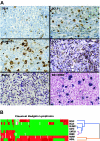
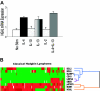
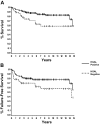
The human germinal-center-associated lymphoma (HGAL) gene and its cognate protein are expressed in a germinal center (GC)-specific manner. Its expression in classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) prompted us to address whether HGAL expression could distinguish biologically distinct subgroups of cHL. Tissue microarrays from 145 patients treated with curative intent showed HGAL staining in 75% and was closely correlated with MUM1/IRF4 (92%) expression. BCL6 (26%), CD10 (0%), BCL2 (31%), Blimp1 (0.02%), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (20%) showed no specific correlation; neither did phospho-STAT6, a key mediator of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling that induces HGAL and is implicated in cHL pathogenesis. In our study cohort, the 5-year overall survival (OS) correlated with young age (less than 45 years, P < .001), low stage (stage I and II, P = .04), and low International Prognostic Score (P = .002). In univariate analysis, HGAL expression was associated with improved OS (P = .01) and failure-free survival (FFS) (P = .05) but was not independent of other factors in multivariate analysis of OS or FFS. The expression of the GC-specific marker HGAL in a subset of cHL suggests that these cHLs retain characteristics of GC-derived lymphomas. The association with improved OS in univariate but not multivariate analysis suggests that HGAL expression is related to known clinical parameters of improved survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kuppers R. Molecular biology of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Adv Cancer Res. 2002;84:277–312. - PubMed
-
- Kanzler H, Kuppers R, Helmes S, et al. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg-like cells in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia represent the outgrowth of single germinal-center B-cell-derived clones: potential precursors of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 2000;95:1023–1031. - PubMed
-
- Bechtel D, Kurth J, Unkel C, Kuppers R. Transformation of BCR-deficient germinal-center B cells by EBV supports a major role of the virus in the pathogenesis of Hodgkin and posttransplantation lymphomas. Blood. 2005;106:4345–4350. - PubMed
-
- Chaganti S, Bell AI, Pastor NB, et al. Epstein-Barr virus infection in vitro can rescue germinal center B cells with inactivated immunoglobulin genes. Blood. 2005;106:4249–4252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

