A randomised study of peginterferon and ribavirin for 16 versus 24 weeks in patients with genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 16956917
- PMCID: PMC1856839
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.102558
A randomised study of peginterferon and ribavirin for 16 versus 24 weeks in patients with genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: The recommended treatment for patients infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 2 (HCV2) is pegylated interferon (peginterferon) and ribavirin for 24 weeks.
Aim: To assess whether a shorter 16-week treatment is as effective as a standard 24-week treatment.
Methods: Patients with HCV2 infection were randomised in a 1:2 ratio to either 16 weeks (n = 50) or 24 weeks (n = 100) of treatment with peginterferon alpha-2a (180 mug/week) and weight-based ribavirin 1000-1200 mg/day, with a 24-week follow-up period. A rapid virological response (RVR) was defined as seronegative for HCV RNA at 4 weeks of treatment, and the primary end point, sustained virological response (SVR), as seronegative for HCV RNA at the 24-week follow-up.
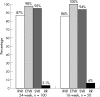
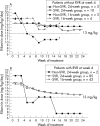
Results: The rate of RVR and SVR was 86% (43/50, 95% confidence interval (CI) 76% to 96%) and 94% (47/50, CI 87% to 100%), respectively, in the 16-week group, which was comparable to 87% (87/100, CI 80% to 94%) and 95% (95/100, CI 91% to 99%) in the 24-week group. Patients with RVR had a significantly higher SVR rate than patients without RVR in both 16-week (100% vs 57%, p = 0.015) and 24-week groups (98% vs 77%, p = 0.002). Multivariate analysis showed that RVR and age were independent factors associated with SVR. Both treatment arms were equally well tolerated. The incidence of alopecia was significantly higher in the 24-week group (49%) than in the 16-week group (20%, p = 0.001).
Conclusion: 16 weeks and 24 weeks of peginterferon treatment with weight-based ribavirin at a dose of 1000-1200 mg/day provided equal efficacy in patients with HCV2 who achieved RVR at 4 weeks.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
-
- Bukh J, Miller R H, Purcell R H. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus: quasispecies and genotypes. Semin Liver Dis 19951541–63. - PubMed
-
- Poynard T, Yuen M F, Ratziu V.et al Viral hepatitis C. Lancet 20033622095–2100. - PubMed
-
- Dai C Y, Chuang W L, Chang W Y.et al Tumor necrosis factor‐alpha promoter polymorphism at position ‐308 predicts response to combination therapy in hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 200619398–101. - PubMed
-
- Fried M W, Shiffman M L, Reddy K R.et al Peginterferon alfa‐2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002347975–982. - PubMed
-
- NIH NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002. NIH Consens State Sci Statements 2002191–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical